Author: Melbicom
Blog

Safeguarding Privacy in Adult Entertainment: Data Security & Compliance on Dedicated Hosting
The adult entertainment industry demands privacy; users’ discretion is paramount; regulators demand strict control; and the data is attractive to attackers, as shown through past failures such as the AdultFriendFinder breach, which exposed around 412 million accounts, including profiles that had supposedly been deleted. Another example would be the almost 10 billion records, including emails, payment logs, and partial credit-card information, that were exposed as a result of database misconfiguration at CAM4.
Data revealing sexual preferences, browsing history, and identity documents is high-stakes. They can be used for extortion and social harm, with devastating reputational damage. All of these considerations drive the modern bar for security and compliance higher, meaning dedicated hosting must be combined with a rigorous governance program to ensure a professional security posture for any serious adult entertainment operation.
Choose Melbicom— 1,000+ ready-to-go servers — 20 global Tier IV & III data centers — 50+ PoP CDN across 6 continents |
 |
Threats Emerging in Adult Content Hosting and the Ever-Tightening Compliance Net
Adult platforms have to tackle two problems simultaneously: they must protect extremely sensitive data while complying with privacy laws that are constantly growing stricter. Data surrounding sexual lifestyles is as sensitive a subject as it gets, and within the EU, GDPR backs that classification with fines up to the greater of €20 million or 4% of global revenue.
Over twenty U.S. states have privacy laws that include notice, access, deletion, and security obligations akin to GDPR models. Several states have age-verification mandates, many requiring government IDs. The Supreme Court upheld Texas’s age-verification law, signaling a verify-first, privacy-questions-later policy direction. Not all states are on board, and some consider collecting age-verification data an increased breach risk; regardless, many adult sites must now collect and process identity documents they hadn’t before.
The obvious problem is that identifying data collection conflicts directly with the adult industry’s previously long-standing promise of anonymity, which, as expected, has made users wary. Concerns surrounding how that information will be handled and protected have arisen, as shown by recent UK surveys. The only real way to bring any ease to the situation is to adopt a privacy-by-design stance by limiting what you collect in the first place, segregating what is kept, encrypting everything, and allowing users control over data retention and deletion. Infrastructurally, that means making wise choices about data locality, tenancy, identity boundaries, and ensuring you verify and monitor continually. Opting for single-tenant hosting helps make these security choices easier to execute and safer than they would be in a multi-tenant hosted environment.
Modern Safeguarding Control: Encryption, Least Privilege, & Zero Trust Policies

An encryption baseline: Encrypting everything both in transport and at rest is a must. Transport-layer encryption (HTTPS/TLS) works across websites, APIs, and streaming to reduce the risk of eavesdropping, protecting the tens of millions of visitors to major adult site networks. Encryption at rest turns plaintext into something undecipherable, helping to keep user databases, logs, and backups safe from attackers hoping to get their hands on any identifiers through grabbing disks or snapshots.
Anonymous, limited collection: Minimizing what you collect is an obvious way to reduce risks. Where collection is necessary, be sure to anonymize it, unless there is a legal or business-critical need. Try to keep usernames pseudonymous and partial, aggressively aggregate analytical data, and hash identifiers. Dropping or transforming IP addresses and session data after short retention periods is also another smart consideration.
Hardening identities: Hash passwords with memory-hard algorithms such as Argon2 or bcrypt and unique salts. Avoid plaintext and unsalted SHA-1, which in prior breaches doomed many operators. Admin and developer access should be bolstered with mandatory multi-factor authentication, which should also be extended to user access. Further measures to employ are isolating credentials, rotating secrets, and separating production and staging to ensure that no compromised test or staging can access production.
Least privilege principles and network segmentation: The principle of least privilege should be applied to both humans and machines by limiting the level of access, which reduces risks significantly. Use web-tier segmentation within your network data to ensure high-level data is untouchable, isolate databases on private networks, and enforce all east-west traffic through encrypted channels with authentication in place. With flat networks and broad entitlements, the loss is drastically higher as seen in historical breaches.
Operate with “zero trust” with constant verification: Irrespective of the origin, every single request should be authenticated and authorized, and there should be constant monitoring to detect any anomalies early on. Unusual volumes of data being pulled should be a red flag, whether the request is from an admin or not, as it is a sudden, multiple API tokens accessing across regions. Containment should be automated for such anomalies to reduce the consequences. Rapid containment can help lower the cost of a breach, which can be hefty. The average global cost of a breach is somewhere in the region of $4.9 million, but companies with instrumentation and alerting reduce their risks with measurable ROI.
Patching, preparation, and testing: Security needs to be an integrated part of operations; catastrophic incidents start out as ordinary flaws, so it is imperative to stay on top of patches and testing to make sure your configurations are correct. Your SDLC should be security-focused, use SAST/DAST to help, and schedule pen tests. Your incident-response plan should include credential rotation, containment steps, and regulator/user notification workflows, all planned strategically to stay prepared. The last thing you want is to be left to figure it out live.
Why Dedicated Hosting Is the Control Plane for Private, Compliant Delivery

The boundaries within shared environments are obscure, whereas the boundary of a dedicated server is explicit. The isolation provided by a single-tenant host hands much more control to adult industry operators who are juggling data sensitivity, regulatory risks, and high-volume traffic. With dedicated hosting, the performance is predictable, ensuring positive user experiences with high content delivery while also handling pinned software baselines, hardened kernels, private management networks, and bespoke firewall policies. All of which is far less practical in multi-tenant environments.
Data locality and residency: Operators must comply with GDPR, SCCs, and state-law analogs, justifying cross-border flows. It is far easier to demonstrate that your EU data is staying in the EU on EU hardware when you can choose the facility and show where disks and backups are. At Melbicom, you can choose a dedicated server in one of our 20 global locations, which includes Tier IV and Tier III facilities in Amsterdam and Tier III sites in other regions. With our setup, your teams get an operational model that ensures that EU user tables are on EU hardware, while North American audiences can stream latency-sensitive content closer to home.
Uncompromised performance: To run constant encryption and zero-trust, you need adequate CPU and network headroom. The dedicated servers we have ready to go at Melbicom support up to 200 Gbps per server, which means no compromise on TLS or any need to throttle deep packet inspection while streaming at peak. Our 1,000+ ready-to-go configurations match CPU, RAM, NICs, and storage to workloads, handling any load surges.
Protected origins through edge distribution: Origin exposure risks are reduced by using a global CDN, which improves delivery and reduces latency at the same time. Melbicom has a CDN that spans over 50 locations. It works to cache static assets and video segments locally to viewers, preventing spikes at the core, and absorbs noisy traffic through WAF/bot controls, and ensures that origin IPs stay private, while reducing latency. Confidentiality is further preserved because TLS is maintained all the way to the user device.
Assured operation: Regardless of how strong your security stance is, if the programs fail at 3 a.m. and nobody acts, you are in hot water. To make sure you have help on hand, whatever the hour, Melbicom provides free 24/7 support, making it easy to isolate a host, revoke keys, or validate network behavior, freeing up your engineers to triage. That kind of support not only assures operations but reduces containment times and limits regulatory exposure and brand damage.
Why use secure dedicated servers for adult sites?
Single-tenant isolation prevents ‘noisy-neighbor’ bleed-through, eliminating hypervisor co-tenancy uncertainty so you can deliver a consistent UX and demonstrate tenancy for compliance. Kernel versions, crypto libraries, and ciphers are controlled and managed by you, and you own the SSH policy, meaning you can gate every administrative action and make sure everything aligns with your security model and compliance obligations.
Solutions for adult content compliance
Compliance should be built into workflows, which is easily facilitated with dedicated hosting because you can segregate identity-verification data on a fenced cluster and give it a shorter retention period and extra encryption. You also have the architecture to handle everything regionally, pinning EU tables to EU racks and restricting backups to encrypted volumes in approved regions. This makes auditing a breeze and ensures user access and deletion are reliable.
Preserving privacy in adult entertainment
Collecting less data, transforming it early, and encrypting everything with vigilant monitoring throughout helps to give users the anonymity they expect. It takes a mixture of strong verification, encryption, and constant monitoring to make sure viewing history and payment metadata is unreadable if it is somehow intercepted.
A Practical Blueprint For Implementation

1) Map and minimize. Map personal data flows and question the necessity of each, keeping only what is needed, such as account info, payment tokens, viewing logs, and age-verification data. Drop whatever isn´t, anonymize the rest as much as possible, and make sure the retention windows are short.
2) Set boundaries for identities: Separate admins, developers, and service identities behind phishing-resistant MFA and bind production actions such as deployments, schema changes, and credential reads to each, logging the configurations immutably.
3) Environmental segmentation: create separate network segments for frontends, APIs, databases, logging, and verification services. Then, place databases on private subnets that are only reachable via bastions on dedicated management networks.
4) Enforce encryption: TLS should run in both client-facing and service-to-service situations. Disks, snapshots, and backups should be encrypted, and the keys stored in isolated modules, rotated frequently. Don’t neglect to scrutinize logs for inadvertent PII and encrypt or redact.
5) Instrument and rehearse: Centralize your instrumentation to help with vigilance, set a baseline telemetry, and configure alerts for any divergence from the norm. Run practice drills for breach situations, isolating hosts and rotating secrets. Always validate backups and cut clean releases to help ensure your containment methods are as quick as possible, saving money and reputation under real circumstances.
6) Deliberately place data: Deploy regionally to minimize latency and satisfy residency. Melbicom can help with keeping your data centers in strategic hubs for regulation with its Tier IV/Tier III facilities in Amsterdam and Tier III elsewhere.
7) Architect on solid infrastructure: Keep up with your streaming demands and match your security baseline by provisioning dedicated servers that align with your NIC bandwidth and storage layouts. At Melbicom, we reinforce that alignment and support your encryption and streaming workloads using modern CPU instruction-set features.
Providing Durable Privacy at Scale

Given the sensitivity of user data, the persistence of attackers, and the stringency of legal obligations, adult platforms cannot afford to rely on weak promises. They must strive for a winning security posture, one that operates in a privacy-by-design format with single-tenant infrastructure that encrypts heavily, minimizes risks aggressively, and continuously verifies to reduce and confine blast radii. Through dedicated hosting and a global CDN that utilizes segmentation and least privilege, you can give teams better control, data placement, and performance headroom to run without sacrificing security.
To have that control at scale, you need the right footprint, bandwidth, and support. Melbicom operates 20 locations, including Tier IV and Tier III facilities in Amsterdam and Tier III sites elsewhere, and provides up to 200 Gbps per server and a CDN in over 50 cities. With more than 1,000 different configurations ready to deploy and 24/7 support, Melbicom’s platform can help adult industry operators to efficiently provide reliable service and UX while meeting privacy laws and satisfying age-verification obligations.
Launch Secure Adult Platforms Today
Get compliant, high-bandwidth dedicated servers for your adult streaming network in 20 global locations with 24/7 support.
Get expert support with your services.
Blog

Maximizing Efficiency with Windows Dedicated Servers in India
Modern Windows servers are judged on three things (latency to users, uptime during change, and governance, which makes auditors calm without slowing down engineers). When those needs intersect with a Windows dedicated server in India, the calculus changes: being able to have compute in proximity to Indian users can reduce round-trip time from ~150ms (abroad) to 20–50 ms locally, and many organizations report 30-50% faster page loads after moving origins onshore. Add the Digital Personal Data Protection Act’s penalties (fines of up to ₹250 crore, or approximately $30 million) for mishandling personal data, and the case for local, well-managed infrastructure becomes obvious.
Choose Melbicom— Dozens of ready-to-go servers — Tier III-certified DC in Mumbai — 50+ PoP CDN across 6 continents |
 |
This article distills what matters for IT managers running mission-critical Windows workloads: explaining hotpatching, using SMB over QUIC, leveraging Windows Server 2025 on Indian dedicated hardware, automating deployments with PowerShell, managing licensing costs, and using Azure Arc to make compliance routine. We will conclude with the practical benefits of ERP and .NET applications, where milliseconds and maintenance windows directly translate to business results.
Windows Server 2025: the Efficiency Toolkit for a Windows Dedicated Server in India
Windows Server 2025 brings cloud-grade capabilities on-premises. On a Mumbai dedicated server, these features directly reduce downtime, speed remote access, and increase utilization – without a forklift rearchitecture.
Hotpatching: security updates without the routine reboot tax
The monthly “patch, reboot, hope” dance is considered a productivity drain. Hotpatching applies patches in memory and keeps things up and running; only occasional “baseline” patches require a reboot. In practice, that changes a dozen planned reboots to about four per year, and it reduces the vulnerability window. On a revenue-bringing system, those saved windows are important: industry estimates calculate data-center downtime to be ~$9,000 per minute. Hotpatching requires modern Windows Server (2022/2025), Secured-Core capable hardware & an Azure Arc connection for orchestration. The service is usage-priced about $1.50 per core/month; a rounding error compared to lost transactions or deferred patching risk. For Indian deployments, this is the path of least resistance to continuous compliance and continuous availability: patch as soon as possible and keep ERP and identity services online; don’t schedule after-hours outages just to be secure.
SMB over QUIC: fast, VPN-free file access online
SMB over QUIC is updating file services for the distributed age. Using QUIC (UDP + TLS 1.3) over port 443, clients connect to Windows file shares securely and without a VPN, with less handshake latency and better performance over lossy networks than TCP. On a Windows dedicated server hosting in India, that means branch offices abroad and mobile teams can pull artifacts, media, or backups quickly and safely, even across variable last-mile links. It also eliminates VPN bottlenecks that increase latency. Pair QUIC with the 1-40 Gbps per server uplinks available in Mumbai, and you can make remote file access feel local, which improves everything from build times to report generation. Governance isn’t sacrificed: access remains TLS-encrypted end-to-end, with Windows Server 2025 enabling auditing and granular client restrictions for QUIC endpoints.
Automate Deployment with PowerShell and CI/CD pipelines
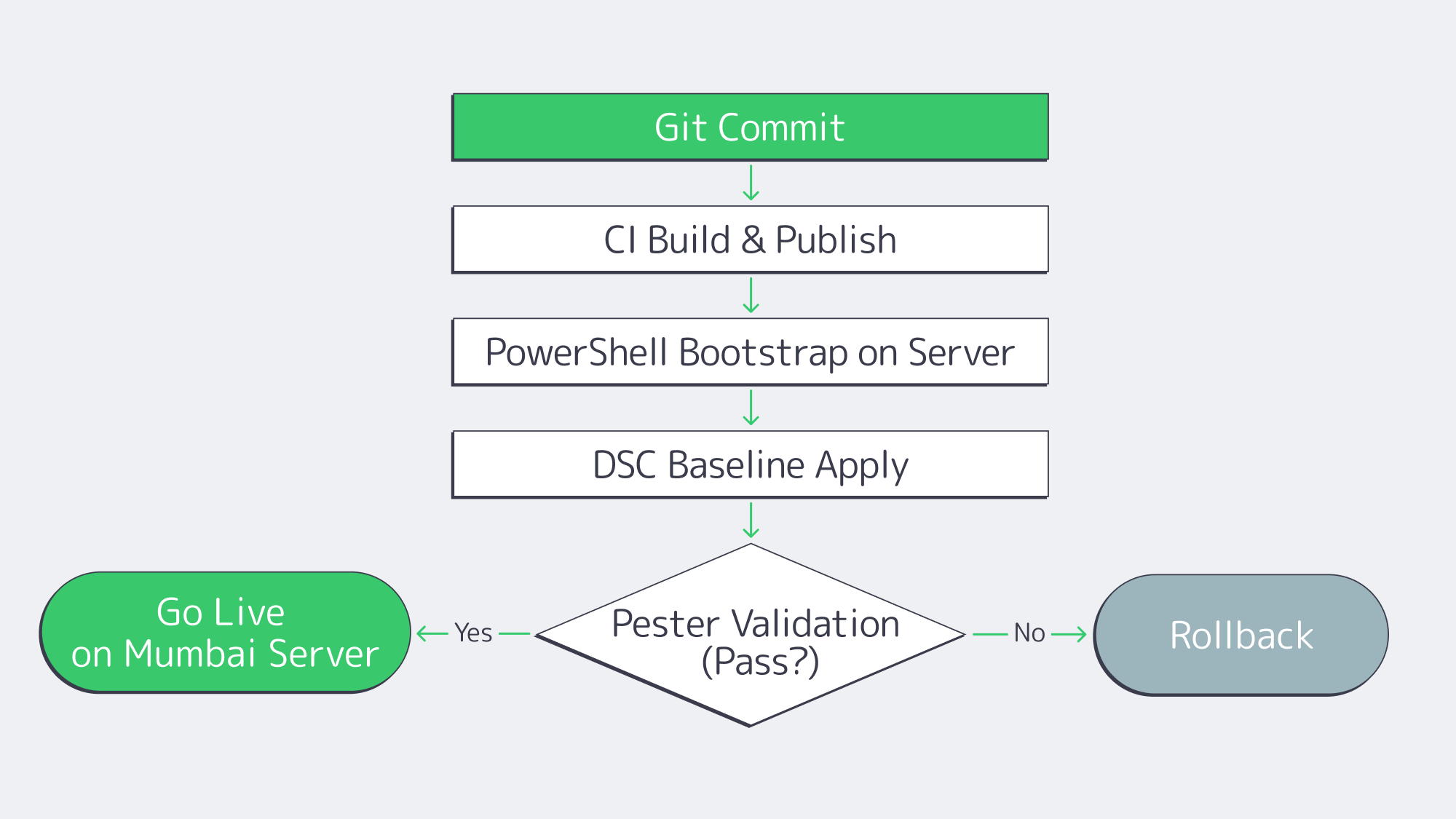
Cloud-like speed on dedicated hardware comes from treating servers like code. A PowerShell-first pipeline avoids drift and makes rollouts, rebuilds, and rollbacks predictable across dedicated servers in Mumbai and other regions.
# Idempotent Windows server bootstrap (excerpt)
# 1) Join domain, 2) install roles/features, 3) harden, 4) deploy app, 5) validate
Start-Transcript -Path C:\Logs\bootstrap.txt -Append
Add-Computer -DomainName corp.example.com -Credential $creds -Force
Install-WindowsFeature Web-Server, NET-Framework-Features, FS-FileServer -IncludeManagementTools
# Baseline hardening via DSC or policy
Start-DscConfiguration -Path .\Baselines\Win2025-Secured -Wait -Verbose -Force
# App deployment
.\Deploy-App.ps1 -Package .\drop\erp-api.zip -Config .\configs\erp-api.json
# Validation
Invoke-Pester .\Tests\postdeploy.tests.ps1 -Output Detailed
Stop-Transcript
Back this up with GitHub Actions or Azure DevOps: On commit, the pipeline runs linters for PowerShell, builds artifacts, applies DSC baselines, runs Pester tests, and registers servers for monitoring. For day-2 operations, Windows Admin Center and Azure Arc unify at-scale patching (including hotpatch orchestration), and inventory. The result: the time-to-ready for a new dedicated server in India is reduced from days to minutes, and reproducibility facilitates audits.
Cost-Aware Windows Licensing on Dedicated Servers in India
It’s at licensing that “predictable” becomes “affordable.” The right mix depends upon virtualization density, CAL requirements, and if you prefer CapEx or usage-based OpEx.
| Edition | Virtualization rights | When to use |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Server Standard | 2 VMs per 16 licensed cores | Single host with 1–2 VMs (e.g. app + DB). Can stack to 4 VMs when licensing again, beyond that consider Datacenter. |
| Windows Server Datacenter | Unlimited VMs/containers on licensed cores | Use Datacenter when you need dense virtualization or heavy use of Windows containers; it’s typically more cost-effective than stacking Standard licenses once you exceed 2–3 VMs. |
Three levers ensure that the dedicated server cost in India remains in check:
- Edition fit: choose Standard or Datacenter licence options based on current VM count and projected growth.
- CALs and RDS CALs: Don’t let client access licensing sneak up on you as a surprise line item. If users/devices access AD, file sharing, or RDS on your server, budget CALs upfront.
- Azure Arc pay-as-you-go: Arc can enable usage-metered Windows Server licensing at $0.046 per core-hour (i.e. $33 per core/month) – useful when environments are cyclical, or if you wish to have OpEx alignment. For always-on systems, compare 12- to 36-month TCO vs. traditional licensing.
Finally, confirm what your host bundles. We at Melbicom offer the Windows licensing through the platform and so you can purchase a dedicated server in India with the OS pre-installed as well as a predictable monthly cost; no surprises on the last mile.
Hybrid Compliance and Unified Ops with Azure Arc
Arc turns on-premises Windows servers into first-class, centrally governed resources – without moving data offshore. That is important when operating under the privacy regime and sector standards (ISO, PCI DSS etc.) for India.
Why it helps:
- Uniform policy & evidence: Consistently apply Azure Policy for ensuring encryption, firewall, and baseline settings across all Arc-connected hosts; export compliance status for auditors across dedicated servers in India and cloud VMs alike.
- Operational consistency: Use of Azure Update Manager to coordinate patching (including hotpatch cadence) and Windows Admin Center for day-to-day tasks – one control plane, many servers.
- Data sovereignty, global oversight: Telemetry, control to Azure; regulated data stays onshore. With DPDP obligations and fines amounting to as much as ₹250 crore (~$30 million), the separation makes good sense.
- Resilience options: Tie in with backup/DR / selective scale-out without undermining locality: Keep authoritative data in Mumbai, burst stateless services when needed.
What it Means for ERP and .NET Workloads
ERP: near-zero maintenance windows, onshore system performance
ERP backbones (e.g., Dynamics, SAP application tiers) hunger for uptime and predictable latency. Hotpatching eliminates the monthly reboot tax, and patch cycles become no-downtime events; planned maintenance becomes an occasional baseline. Over a year, that’s hours of production time reclaimed – material when $9,000/minute is the going rate for outages. Hosting the ERP tier and file integrations on a dedicated server in Mumbai reduces interaction latency from ~150ms to 20-50ms, and for many workloads, user-perceived load times improve by 30-50% after localization.
For resilience, Windows Storage Replica (with compression) maintains a warm copy in another metro of India with minimal bandwidth. Add SMB over QUIC for branch file drops and backups: secure, VPN-free, tolerant of spotty last-mile links. The net is a cleaner operating posture – patch fast, replicate efficiently, keep data local, and keep users unaware that maintenance happened at all.
.NET: throughput, tail latency, and acceleration
Custom .NET estates benefit along two axes.
- Network throughput: Windows RSC/USO offloading allows servers to push much more UDP and mixed traffic at a lower CPU cost. Combine that with the connectivity in Mumbai (up to 40 Gbps per server) and API backends, media services, and telemetry pipelines can breathe.
- Density & predictability: More containers or VMs running on Windows on a Datacenter licensed host increases consolidation and helps to tamp down p95/p99 tail latency vs. noisy multi-tenant pools; users feel the difference during checkout and peak events.
Operationally, a PowerShell pipeline will provide you with blue/green or canary releases on a dedicated host just as well as in the cloud: deploy packages, run Pester validations, flip traffic and roll back instantly; no manual “click ops.”
Conclusion
Windows Server 2025 filled some long-standing loopholes for on-prem Windows: Hotpatching makes security a background task rather than a cause for downtime. SMB over QUIC makes remote file access modern without the VPN tax. On a Windows dedicated server in India, these features provide what stakeholders see – snappier response, fewer service windows, better utilization of resources, while Azure Arc and PowerShell automation ensure that operations are compliant and repeatable. The architecture does not need to be exotic; it needs to be close to users, easy to patch, cheap to run at scale, and simple to prove compliant.
For IT managers looking to prioritize ERP and .NET performance, the path ahead is pragmatic: bring computing to Mumbai to tame latency, adopt hotpatching to reclaim nights and weekends, use QUIC to make secure access and integrations easy, and codify the environment so rebuilds are a non-event. The outcome is measurable, not theoretical: faster transactions, fewer incidents, and steadier audits.
Ready to deploy in India
Get a Windows dedicated server in Mumbai with up to 40 Gbps bandwidth, Windows licenses, and 24×7 support — delivered in hours.
Get expert support with your services.
Blog

Implementing HA Storage on Dedicated Servers for Zero Downtime
Downtime must be considered more than an inconvenience; it is an existential risk. The average cost of an outage is approximately $9,000/minute. In this modern technological era, many companies are looking for 99.98% availability for their major systems. The path to those numbers is not a rigid SAN or manual runbooks; it is a cohesive blueprint that treats failure as routine and plans for it.
This article distills the blueprint for HA dedicated storage on dedicated servers, featuring RAID 10 for local resilience, synchronous replication across nodes, quorum-based clustering to prevent split-brain failure, and automated failover orchestration to ensure instant and deterministic recovery. We will also cover GlusterFS and DRBD-based mirroring for zero-downtime updates, and briefly contrast legacy single-controller SANs to reinforce the case for why the distributed model has won out.
Choose Melbicom— 1,000+ ready-to-go servers — 20 global Tier IV & III data centers — 50+ PoP CDN across 6 continents |
Blueprint: HA Dedicated Storage that Assumes Failure
- Local protection on each server (RAID 10).
- Synchronous replication across peers (no data-loss failover).
- Quorum + Witness to arbitrate (leadership) & avoid split-brain.
- Automated failover to switch service endpoints with no human intervention.
This “defense in depth” transforms disk, server, or network failures into non-events while preserving performance.
RAID 10: Local Redundancy without the Rebuild Penalty

RAID 10 (mirrors striped across pairs) has two benefits that are vital to HA – rapid rebuilds and low write latency. When a disk fails, the array does not use parity math; instead, it mirrors, so rebuilds are faster and risk windows are shorter. That’s important in clusters, because you never want a node degraded for long in production. RAID 10 also maintains throughput and predictable latency under load, which prevents the synchronous replication pipeline from stalling. On modern dedicated servers, combining RAID 10 with enterprise SSDs or NVMe drives provides sufficient IOPS headroom for replication and client I/O to coexist without contention.
Synchronous Replication: Zero-Data-Loss Failover Design
RAID is a protection for the node, and replication is a protection of the service. With synchronous replication, a write is acknowledged only when it lands on both nodes, resulting in an RPO of zero. In a two-node design, if a node fails (Node A), Node B has a bit-for-bit current copy of the data and can take over immediately.
This requires a high-speed deterministic interconnect between nodes – dedicated 10/25/40 GbE or faster, preferably isolated from client traffic. In designs that demand strict separation, Melbicom can provide the use of VLAN-segregated links for replication and heartbeat, ensuring storage traffic remains clean and predictable. Low, consistent latency avoids write stalls; plenty of bandwidth absorbs bursts. Melbicom’s dedicated servers can be provisioned with high-throughput links (up to 200 Gbps per server, where available), which provide the headroom that replication traffic needs while applications run at full speed. Keep cabling, NICs, and switch paths symmetric across nodes to prevent asymmetric latency that can pass itself off as “flaky storage.”
Two proven approaches:
- Block-level mirroring (DRBD): Mirroring disk blocks in lockstep, in essence, a networked implementation of a form of RAID1. Commonly deployed in an active-passive configuration: one node mounts the volume, the peer tracks every write, and is promotable in the event of failover.
- Replicated file storage (GlusterFS): Files are replicated across nodes, and any node can serve files from any replica (active-active). Clients continue through surviving nodes in outages; self-healing processes fill gaps on return of a node.
Two-node + witness (sync replication)
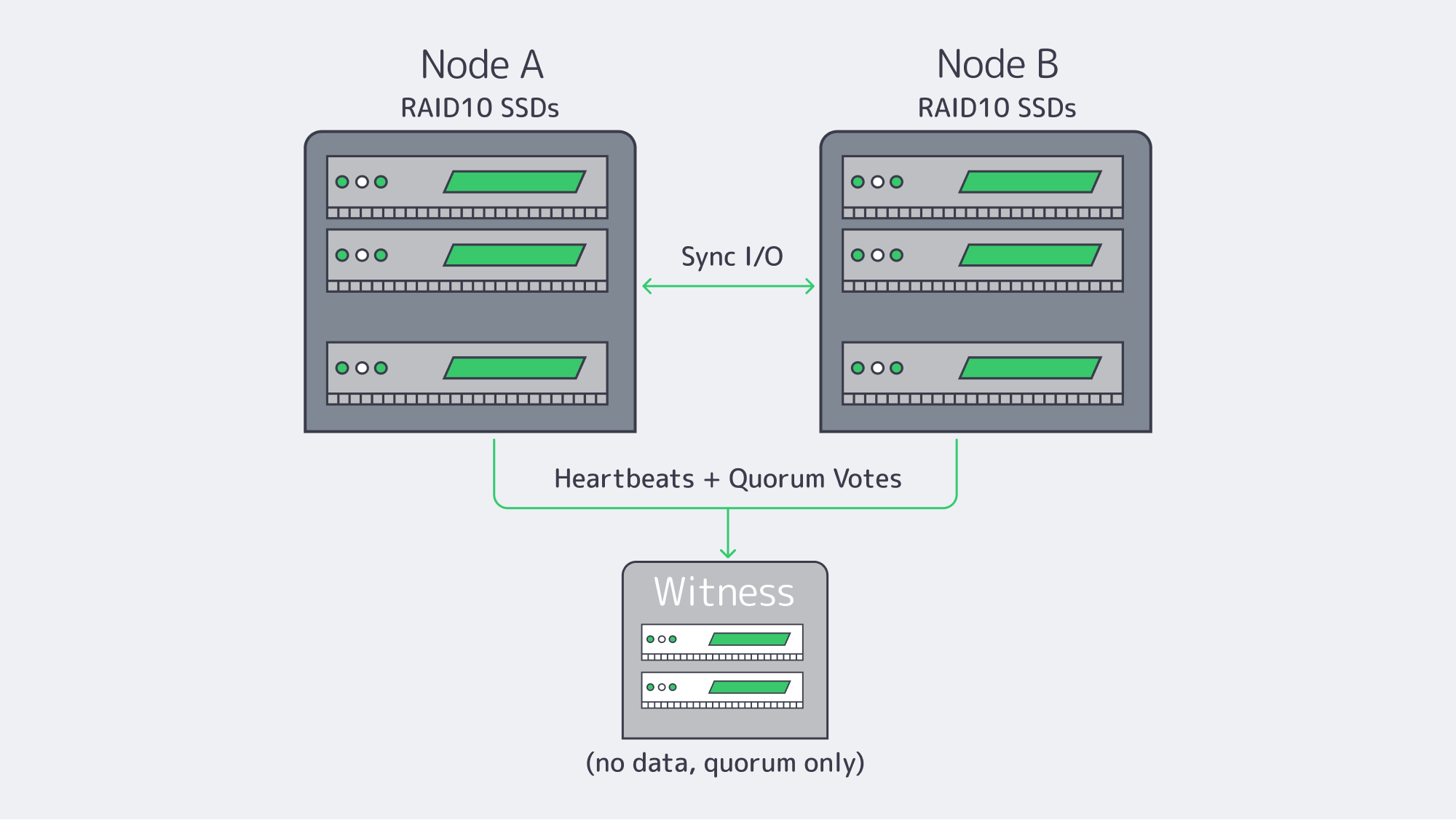
Quorum, Witness Placement, and Split-Brain Prevention Essentials
Nothing torpedoes an HA storage system quicker than split-brain – two nodes accepting writes independently after a partition. The antidote is quorum; actions that could change the data require a majority of votes. In a two-node storage cluster, you should add a witness (qdevice/arbiter) so there are three votes. If Node A and Node B lose contact, the side still in contact with the witness remains authoritative. The other stands down and is fenced if required. This maintains one linear history of writes.
Placement definitely matters a lot. Place the witness in a separate fault domain, ideally, a different rack/room or even a different Melbicom site, so that the loss of one location doesn’t also take out the tiebreaker. The witness is light-weight (no application data), so a tiny VM is all that is needed. For N>=3 data nodes, make sure there is an odd number of votes or add an external quorum device.
Fencing (STONITH) is the second part of the safety net. If a node loses quorum or is unresponsive, the cluster must power off or isolate it before promoting a peer. This removes “zombie” writes and ensures that when the node returns, it returns as a clean follower and is ready to resync. For this reason, use IPMI or an out-of-band API independent of the data network to ensure fences succeed even if there is a network incident.
Automated Failover Orchestration and Consistent State Recovery
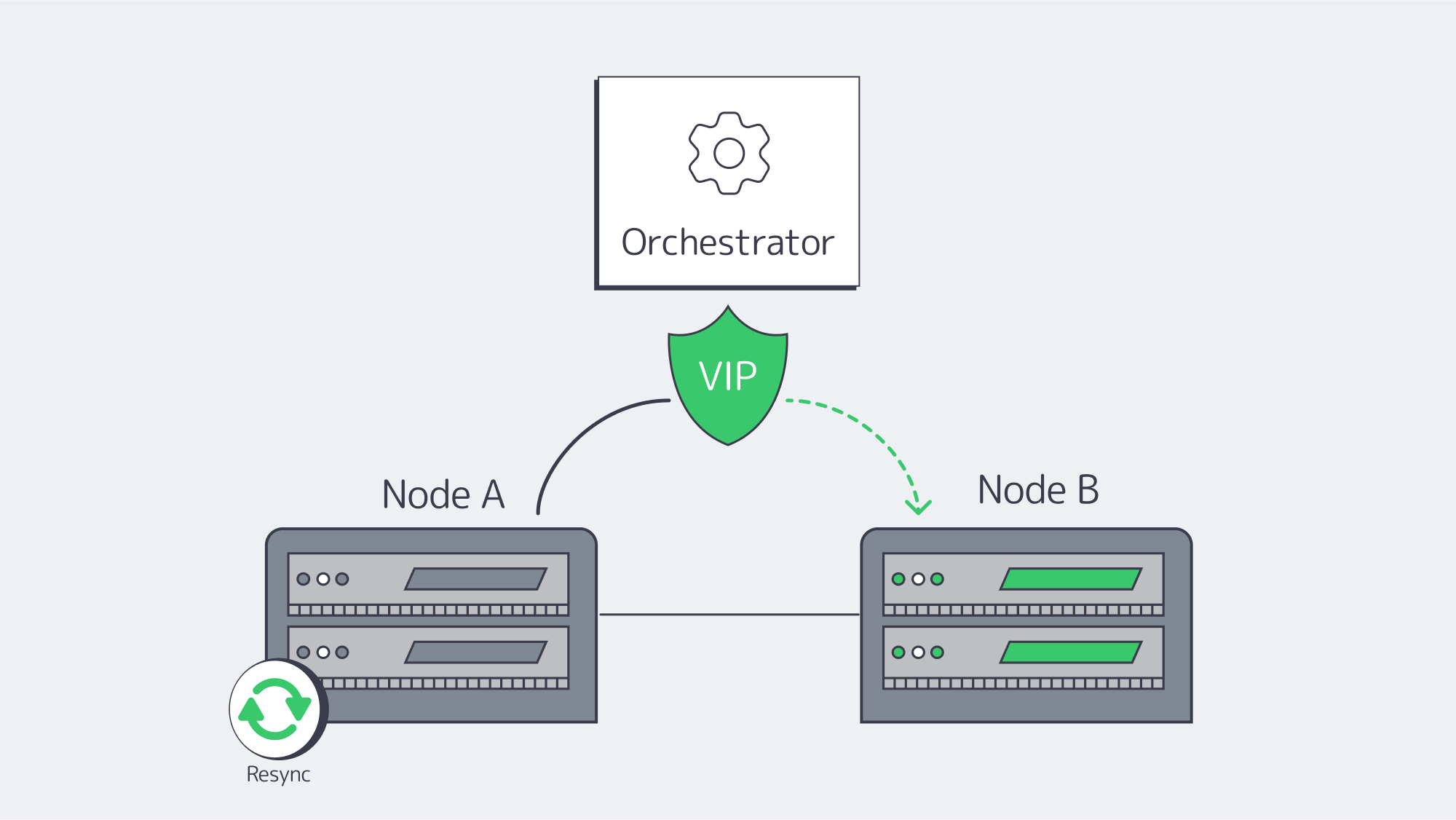
High availability doesn’t work if a human has to step in. Automated orchestration identifies failures and migrates service identities (virtual IPs/exports/LUNs) to healthy nodes within seconds. On Linux, Pacemaker + Corosync is the canonical stack: Corosync is responsible for membership/heartbeat; Pacemaker handles resources, ordering and constraints.
A common DRBD+filesystem+export failover workflow:
- Fence the failed primary.
- Promote DRBD on the secondary to Primary.
- Mount the filesystem and start the export service.
- Assign a service IP (or flip DNS/LB target).
For consistent state recovery, whenever nodes are returning, they cannot ever serve stale data. Depend on the built-in journals and resyncs of the storage layer:
- DRBD does an incremental resync of changed blocks.
- GlusterFS self-heals to reconcile file replicas.
Keep orchestration conservative: wait for “UpToDate” replication states before re-admitting a node, and codify stringent resource-ordering to prevent timing races. Finally, test: simulate power pull, NIC failures, split links, until metrics (failover time, resync duration) are predictable.
Distributed File Systems vs. DRBD Mirroring for Zero-Downtime Updates
Both designs allow rolling maintenance and upgrades without any downtime. Select based on the access model, concurrency, and operational style.
| Technology | Best fit | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| DRBD + FS + Export | Block-level consistency for databases or single-writer filesystems, deterministic failover | Simple active-passive; pair with Pacemaker; add a cluster filesystem only if multi-writer is unavoidable (adds overhead) |
| GlusterFS (replicated) | Shared file namespace with active-active access; NFS/SMB/POSIX clients | Rolling upgrades node-by-node; automatic self-heal; Plan for a small consistency window during heal; tune for small-file or large-file patterns. |
| Ceph (optional) | Scale-out object/block/file; many nodes; multi-tenant | Operationally richer, with more moving parts; strongest in cases where you need elastic capacity and mixed protocols. |
Zero downtime updates applied
- Using DRBD, deliberately migrate primacy: intentionally fail over cleanly to the secondary, patch and reboot the primary, resync and (optionally) fail back. Client I/O notices a short pause during the switch; retries are used to mask it at the app layer.
- With GlusterFS, upgrade one node at a time. The volume is kept online by peers. After nodes return, they check for completion of the healing process before proceeding.
Legacy single-controller SANs struggled here: the box itself had to be upgraded and often required a maintenance window. Distributed HA turns that model on its head; service remains up while parts change.
Operational Checklist
- Homogeneous builds: drives, NICs, and controllers are identical across nodes.
- Dedicated replication fabric: min of 10GbE, isolated from client traffic, symmetric paths, consider dual links.
- Quorum discipline: odd votes; external witness in a separate fault domain; enforce STONITH fencing
- Health gates: only re-admit nodes after full resync/heal; degrade health if the file system is not in good condition (e.g., if the data on a LUN is unreadable) or replication is not running smoothly.
- Fire-drills: quarterly failover drills for power, NIC, and process level faults; Document RTO/RPO.
- Security & compliance: isolate cluster traffic; encrypt where appropriate; keep immutable backups to meet retention mandates; consider S3-compatible offsite copies, cold copies via SFTP backup.
- Geo strategy: keep synchronous pairs metro-close; async replication for regional DR; witness out-of-band placement.
Conclusion: Bringing the Parts Together

Zero-downtime storage isn’t a single technology; it’s a system that anticipates component failures and makes continuity routine. The pragmatic blueprint is fairly clear: RAID 10 for on-box resilience, synchronous replication for node loss, quorum, and a well-placed witness for preventing split-brain, and automated failover to keep humans off the critical path. Add GlusterFS or DRBD-based mirroring to enable rolling updates without maintenance windows and ensure consistent-state recovery, allowing repaired nodes to rejoin safely. The payoff is measured in avoided losses (think $9,000 a minute) and in the quiet confidence of systems that simply don’t blink.
If you are planning a refresh, start small: two identical servers, a dedicated replication fabric, a third witness, and a clear runbook for failover tests. Expand from there as needs expand. The architecture has a nice scale, and adding any node to the system decreases the likelihood of a single fault becoming an incident.
Launch your HA cluster
Deploy dedicated servers with high-availability storage engineered for zero downtime.
Get expert support with your services.
Blog

Dedicated Servers for Blockchain Node Hosting and Staking
Blockchain has long outgrown the playground of hobbyists. Tens of billions of dollars in digital assets ride on the success of not only validators, but of nodes. The margin for error is slim. High-stakes applications demand that networks like Ethereum and Polkadot maintain high availability, achieve low-latency data propagation, and deliver predictable I/O throughput. In that context, blockchain node hosting on dedicated servers moves from “nice to have” to a professional baseline.
Choose Melbicom— 1,000+ ready-to-go servers — 20 global Tier IV & III data centers — 50+ PoP CDN across 6 continents |
3 Elements of Success for Blockchain Node Hosting on Dedicated Servers
Dedicated servers, as single-tenant machines hosted in professionally managed data centers, can provide three key wins that translate directly into validator success: Exclusive resources, paired with continuous server uptime and total management control comprise the dedicated server value proposition.
Exclusive resources and predictable performance
Consensus participation is a time-critical activity: The processes of proposing, attesting, and voting need to occur on strictly scheduled time intervals. Predictable compute performance requires hardware that is unaffected by other users’ workloads, or by the resource allocation decisions made by hypervisors. A dedicated server grants your node an exclusive CPU, RAM and NVMe I/O path. The resulting stability shows in faster block ingestion, fewer missed attestations, and more predictable catch-up performance after restarts. When execution clients and indexers work on RPC endpoints, they need constant IOPS and memory bandwidth to achieve lower tail latencies in their API responses and prevent backlog issues as mempools grow.
24/7 blockchain uptime
Uptime is not a vanity metric; on proof-of-stake networks it’s revenue preservation. Miss enough duties and rewards erode. Prolonged gaps can even trigger penalties on some chains. Purpose-built facilities reduce those risks with redundant power and cooling, multi-homed transit, and on-site technicians. That’s why many operators host validators in Tier III and Tier IV data centers: the engineering goal is 24/7/365 operation with maintenance performed without downtime. Melbicom’s data center portfolio includes Tier IV and Tier III facilities in Amsterdam; other data centers around the world are also Tier III-rated, all engineered with multiple paths for power, cooling, and networking.
Bandwidth ceilings also play a bigger role than you might think. Initial sync and snapshot restores contribute to sustained throughput, but bursty blocks and heavy state transitions drive traffic spikes. With per-server connectivity from 1 Gbps all the way up to 200 Gbps where it’s needed, the extra headroom from Melbicom means you’re far less likely to fall behind your peers when surges happen, which means faster time-to-sync and smoother propagation under load.

Security and control for validator server hosting
Validator keys and signing paths should be strictly isolated. On a dedicated server, you get to control the OS hardening, the kernel, the firewalling, the key storage mechanism, and the monitoring stack without any co-tenants to introduce additional risk. Beyond node-level security, there is systemic flexibility: a significant portion of public nodes are on only a few cloud providers, creating large correlated failure surfaces. Distributing your validators between providers and across geographies not only bolsters decentralization but also dilutes shared-fate risks. With 20 global locations, choosing where to place nodes with Melbicom is easy, making it both resilient and performant.
Scalability without surprises
Networks grow, client footprints expand, and new features such as MEV or PBS tooling introduce background services. Dedicated servers scale in two useful dimensions: vertically (RAM, higher-frequency CPUs, more NVMe) and horizontally (additional servers dedicated to relays, RPC, sentries, indexing, etc.). The overwhelming majority of configurations in Melbicom’s portfolio are ready to rock; operators commonly boot a clone node for rolling upgrades or failover, then power down the older server once cutovers are finished. That process preserves continuity without late-night fire drills or day-of heroics.
Hardware Realities: What Modern Blockchain Networks Expect
The traditional approach of “renting a small VM” or “running a full node on your spare PC” fails to meet modern client requirements or the scale of ledger data. Throughput-optimized newer networks are defined less by a light footprint and more by a shift toward sustained performance. Fast CPUs, generous memory, NVMe SSDs, and reliable bandwidth are the through line across all our target ecosystems, and network interfaces must be fit for purpose to accept and serve sustained ingress/egress without intermittent packet loss.
| Network | Example Node Requirements |
|---|---|
| Ethereum (PoS, consensus + execution) | ~8-core modern CPU at ~3.5 GHz; 64 GB RAM; 4–8 TB NVMe SSD; ≥300 Mbps (preferably 1 Gbps). |
| Solana (PoS) | High-frequency 24 cores (~4.0 GHz); 512 GB RAM; multiple NVMe SSDs (≈6 TB total for ledger + accounts); 1–10 Gbps network. |
| Polkadot (NPoS) | 8 cores at ~3.4 GHz; 32 GB ECC RAM; ≥2 TB NVMe; ≥500 Mbps symmetric. |
| Cardano (PoS) | 4 cores at 3.0+ GHz; 32 GB RAM; ~250 GB SSD; often deployed as a block-producer plus one or more relays for resilience. |
Table 1: Sample full/validator node footprints. Fast CPUs, plenty of memory, NVMe, and low-loss bandwidth are common across ecosystems.
A few patterns worth underlining
CPU frequency is king. Validation, consensus, and block production are latency-sensitive operations; higher per-core clocks keep the critical path short.
RAM cushions instability. As client processes, caches, and state grow, adequate memory headroom is required during sync operations and post-upgrade reorganizations.
NVMe is a must-have. Random I/O has a high share for many clients; SATA SSDs and network-attached storage introduce preventable stalls.
Network bandwidth is not just a number. Operators should consider packet loss, micro-bursts, and route quality among the first-class properties of their network connection, rather than focusing solely on nominal bandwidth.
High-throughput chains such as Solana encounter especially rigorous minimum requirements because their project documentation emphasizes that validator hardware must scale simultaneously with ledger expansion and vote traffic to maintain consensus. In Polkadot, key team members have laid out recommendations along similar lines, guiding serious validators to single-tenant hardware with ECC memory and true NVMe (not just shared, oversubscribed storage) precisely so as to avoid memory and I/O bottlenecks lying dormant. Even Ethereum’s requirements are modest only in comparison to Solana; operators running substantial hardware stacks will often jump to larger NVMe footprints to locally store archival or pruned histories and avoid slow remote calls during spikes.
Top Design Principles for Reliable Crypto Node Infrastructure
Place nodes where latency and resilience intersect
The geographic location of your nodes still matters. Validators located close to major Internet exchange points have been observed to exhibit better peer connectivity and lower path variance, on average. Melbicom operates 20 data centers worldwide to enable our operators to strike a balance: place your consensus and relay nodes strategically, near your peers but spread far enough to reduce correlated disruptions.
Design your network for propagation rather than throughput alone
A 1 Gbps port that never drops packets is superior to a 10 Gbps port with intermittent micro loss. We’ve found that dedicated ports with quality upstreams, ample burst capacity, and fast restoration paths (across diverse providers with shorter downstream routes) are best. We provision per-server bandwidth up to 200 Gbps for special use cases that require it, and a CDN across 50+ locations can take public RPC or static requests off your validator network path, where your architecture requires such isolation.

Standardize on modern CPUs, ECC RAM, and NVMe
Validator workloads are jitter-sensitive. Platforms with modern AMD EPYC and Intel Xeon CPUs, ECC memory, and NVMe RAID provide the deterministic behavior the node software demands. For Ethereum-class footprints, many operators standardize on 64–128 GB RAM and 4–8 TB NVMe. For Solana-class footprints, 512 GB RAM and 2+ Gen4 NVMe drives are the practical minimum to keep accounts DB and ledger hot.
Build for continuous operations
Rolling upgrades and fast recovery are part of the plan. The simplest pattern is two like-for-like servers per critical role (validator + hot standby, block-producer + sibling relay). With 1,000+ ready-to-deploy configurations, we at Melbicom can mirror your primary build in the same metro or second region, then help you cut over during client upgrades or hardware refreshes. Free 24/7 technical support shortens mean-time-to-repair if a component fails.
Deliberately keep RPC and validator roles separate when possible
Mixing public API traffic with consensus work is convenient until it isn’t. A split architecture (validator on one host, RPC/indexing on another) helps isolate unpredictable workloads. On dedicated servers, that separation is cost-effective without sacrificing performance.
Why Outdated Setups Struggle
Consumer gear and oversubscribed VMs underperform for predictable reasons: shared I/O, noisy neighbors, single-ISP exposure, and limited hands-on recovery if hardware fails. Occasional home-lab nodes still have a role in testing and education. But for networks where missed duties lower income, or where your reputation with delegators is on the line, professional, single-tenant servers in Tier III/IV facilities are the cost-effective answer. The calculus is simple: more signed duties, fewer reorg headaches, lower operational risk.
Conclusion
Melbicom’s footprint and network were architected for this moment. With Tier IV and Tier III facilities in Amsterdam and 18 Tier III locations across the globe, per-server connectivity up to 200 Gbps, a 50+-location CDN, 1,000+ configurations ready to deploy, and 24/7 support, Melbicom makes professional-grade validator hosting accessible and scalable. If you’re architecting for the next cycle of network growth, the right move is to put your keys on infrastructure engineered for nonstop duty.
Launch Your Dedicated Validator Server
Deploy a Melbicom dedicated server built for blockchain nodes—fast CPUs, NVMe storage, and bandwidth up to 200 Gbps.
Get expert support with your services.
Blog
Cheap Dedicated Server Hosting in UAE: Risks of Going Low-End
Cheap dedicated server offers in the UAE may well seem very alluring on the surface, promising local presence and lower latency for a minimal monthly fee, but all too often, behind these appealing prices are hidden costs waiting to crawl out of the woodwork.
Typically, performance suffers, hardware is outdated, and support is thin at best. Add to that security gaps, and any “savings” you may think you have made on initial outlay are, in actuality, risks. Modern businesses in the UAE market have matured, requiring low-latency infrastructure that you can depend on, irrespective of budget. To compete, and more importantly, grow, it is wiser to maximize value rather than to simply buy the cheapest box, for if not, you risk your reputation and revenue.
Choose Melbicom— Dozens of ready-to-go servers — Tier III-certified DC in Fujairah — 50+ PoP CDN across 6 continents |
The Evolution of UAE Hosting: Why Value Matters More Than Ever
Once, regional options were scarce and buying into the local ecosystem was pricey, which pushed most to host elsewhere, such as Europe or the US, despite the latency caused by distance. Today, the market has rapidly expanded and shows no signs of stopping, with the Emirati data center market projected to grow from around $1.26 billion to $3.33 billion (17.5% CAGR) by 2030. As capacity has grown, so have expectations, and overall prices have lowered, resulting in affordable dedicated server hosting in the UAE that meets enterprise-grade thresholds, so long as you know how to avoid the pitfalls that come with low-end hosting deals.
The Risks of Cheap Dedicated Servers in the UAE: What Isn’t on the Price Tag
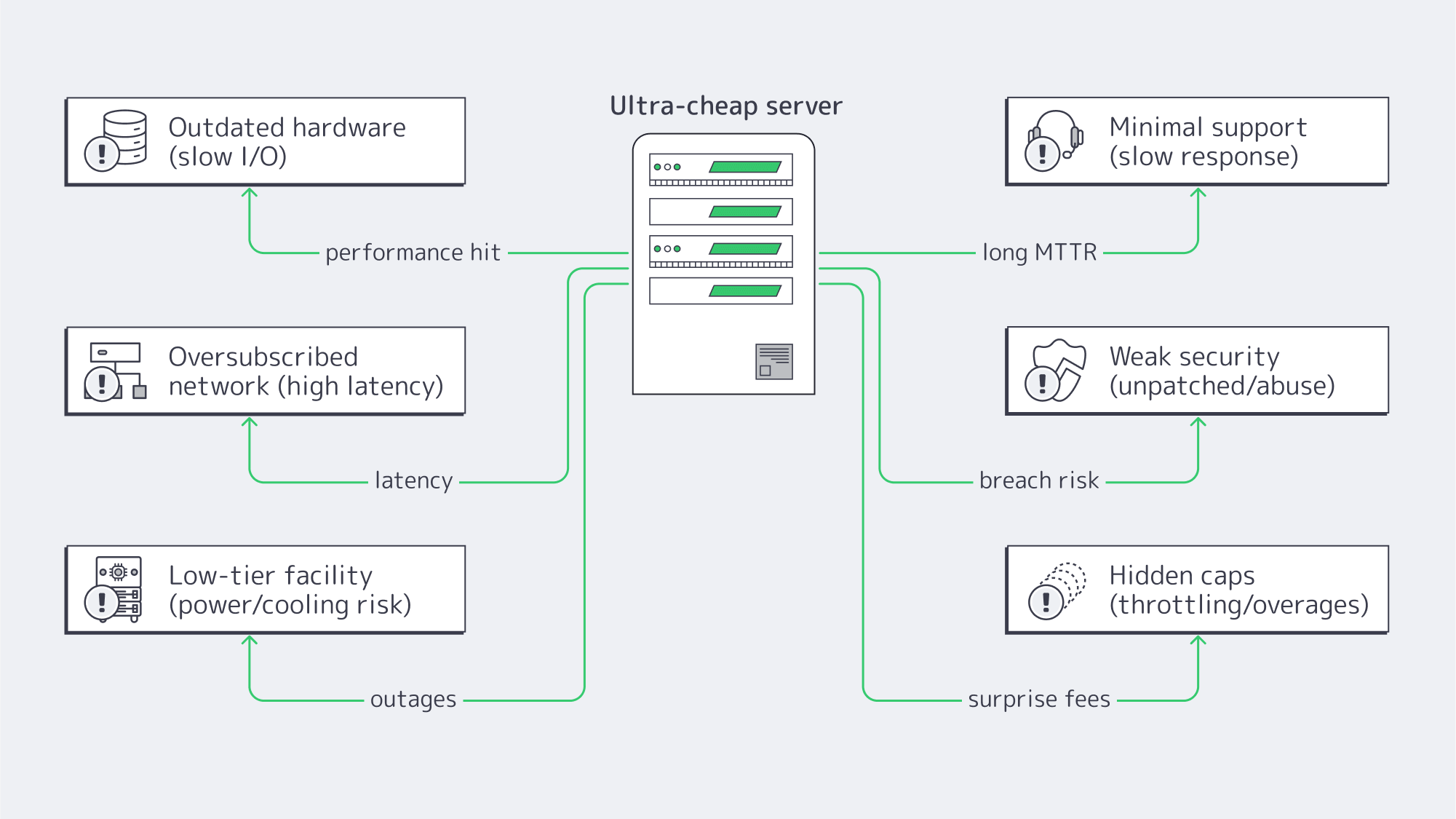
Outdated hardware is hindering performance
Often, ultra-low prices are a result of retired or refurbished gear, which means older-generation CPUs, spinning HDDs instead of SSD/NVMe, and other components that are well past their prime. This directly impacts business because pages render slowly, concurrency drops, and the failure rates rise. When you consider that 47% of modern customers expect a page to load in under two seconds, and that after four seconds, conversion rates sink toward ~1%, then a “cheap” server starts costing you quickly in revenue loss.
Latency advantages quashed by thin networks
The main reason to go hot locally is to slash your round-trip times, but if capacity and peering are inadequate, then cutting the distance to lower latency is more or less pointless. A Dubai–London path sits roughly in the 125–150 ms range; a UAE dedicated server with good connections can serve local users in just a few milliseconds. Local peering and presence can shave user latency in the Middle East by as much as 80% according to a case study, when compared with routing via Europe. Cheaper hosts typically oversubscribe uplinks and their routing is often less diverse, effectively making your local “UAE” server behave like it’s abroad.
Unreliable uptime forfeits the “discount”
Low-end hosts typically operate from low-tier facilities without enough redundancy in place, which equates to unreliable uptime. Tier III data center is engineered to provide 99.982% availability; this margin means roughly 1.6 hours of annual downtime. Downtime is no joke; somewhere between €7,000 and €15,000 are estimated to be lost per hour by small and midsize organizations experiencing IT outages, and larger operations often exceed €100,000 per hour. An hour of downtime can cost more than $300k, according to industry survey reports, with just under 20% of organizations citing $5M and upwards. Downtime risks help put the cheapest providers’ offers into perspective.
Support that makes “cheap” expensive
Response time is key with any issue; should you face kernel panics at 3 a.m., you want support on hand. Cheaper providers rarely provide 24/7 coverage, and those that do often simply have a phone line manned by untrained staff to report the incident, but not to solve it. Long queues equal longer outages, and many turn toward hiring emergency IT specialists or forming in-house teams to counter the lack of support from the provider, which raises your costs considerably. With Melbicom, that hidden cost is eliminated as we provide 24/7 technical support across our dedicated servers, completely free of charge, helping maximize your reliability, resolving issues efficiently to ensure downtime costs don’t spiral.
Accumulating security debt
These low-end facilities are also unlikely to safeguard their environments as thoroughly; they may not be as quick to update and patch firmware and operating systems, and they may even tolerate “bad neighborhood” IP ranges. This leaves you vulnerable to exploitation and security incidents that can spell downtime and ultimately erode trust. What you need is a provider that maintains the current platform, isolates abusive traffic to prevent spillover, and has adequate network safeguards in place. Prevention is key; if not, you risk being blacklisted, having unmanaged traffic abuse, and breaches with devastating consequences.
Other hidden constraints
There are other hidden constraints with a cheap provider; their “dedicated” plans generally offer little flexibility. They are typically fixed, and the hardware is low spec with little in terms of an upgrade path, making it very difficult to scale up should you wish to expand. Rock-bottom also usually means throttled bandwidth with vague “fair use” clauses and hefty fees for overage. Organizations seeking growth are then ultimately forced to migrate and perform manual cutover, data sync, and the inevitable service interruptions effectively erase any “savings” you might have initially made. When searching for a dedicated server in the UAE, you ideally want a provider that allows you to start modestly and step up CPU, RAM, storage, and port speed without a headache.
Dedicated Server Hosting in UAE: What to Prioritize on a Budget
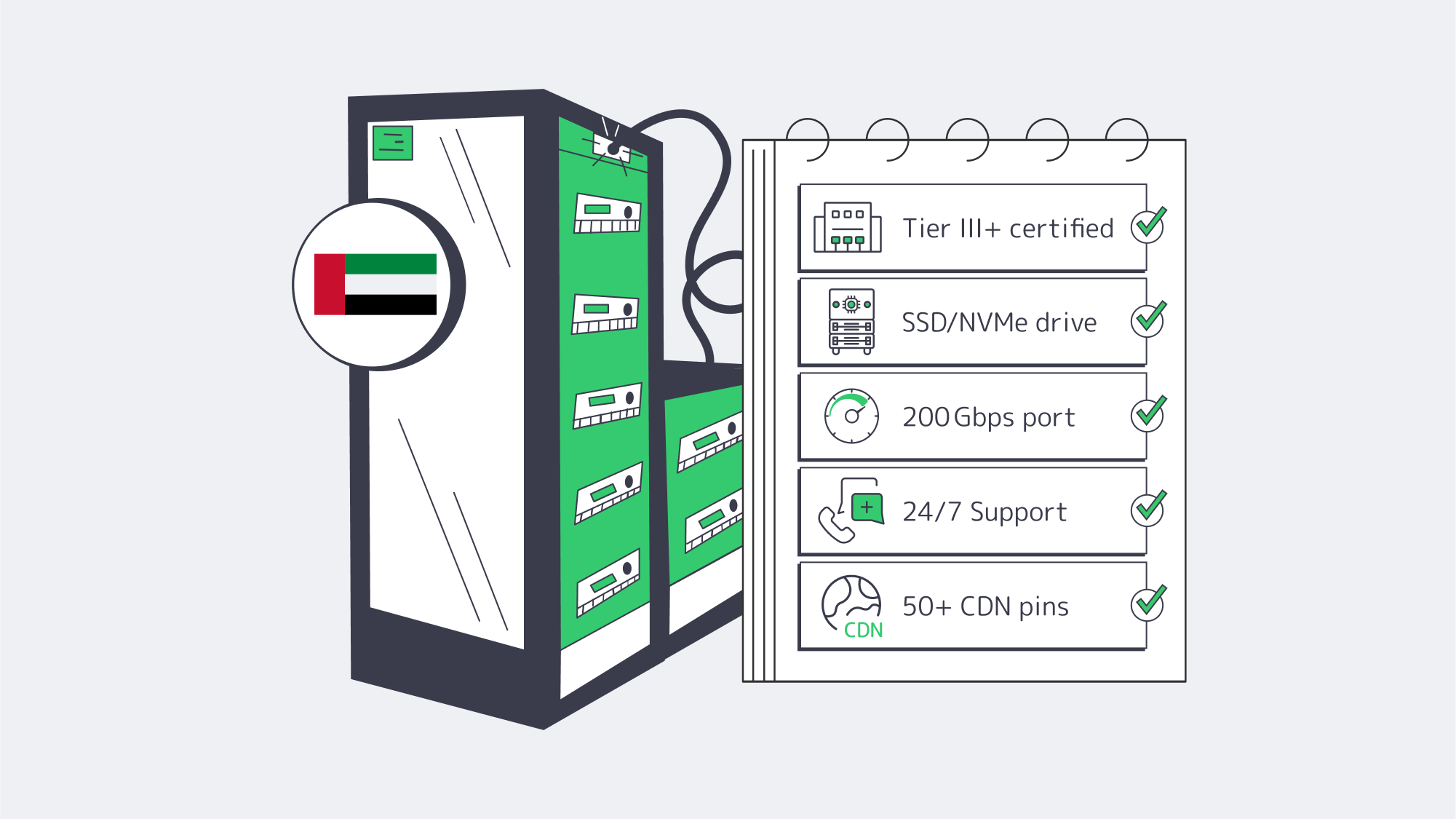
Facility tier and location: The facility is your key variable; look for a tier and location with redundant power, ample cooling, and a high-performance network to minimize your downtime and maximize your workloads. Melbicom’s deployment in Fujairah is a Tier III facility, protecting against the riskiest failure modes. If your provider won’t name the tier, consider it a red flag.
Trustworthy hardware: Cheap hosts often cut the most corners in the hardware department. To reduce failure rates, you want enterprise-grade platforms that support modern Xeon/EPYC, ECC RAM, and SSD/NVMe to speed up operations, run databases, search indexes, and build pipelines. Melbicom has dozens of ready-to-go configurations to deploy, keeping your costs aligned to your workload.
Network routes and real-world latency: The location is only part of your latency equation. Serving content from the UAE itself shortens path length in the Gulf region, but only if the provider peers and keeps headroom. Melbicom pairs its low-latency Fujairah offering with its CDN that has over 50 global locations, so that your dynamic workloads are kept close and static assets are cached wherever your audience is.
Support for incidents: You want to minimize the duration of incidents by choosing a provider that treats operations as a core competence. The 24/7 support offered by Melbicom staff keeps mean-time-to-repair low, meaning you see fewer escalations, faster restores, and remain calm.
Bandwidth transparency and growth path: You want the ability to expand without ceilings, so investigate published port speeds, transfer, and upgrade steps, to know your limits. Melbicom provides high per-server bandwidth of up to 20 Gbps in Fujairah and has simple upgrade paths in place to help your business grow without any unpleasant surprises, bills, or technical debt.
A UAE Server Without the Latency Penalty
Every millisecond counts for flows, dashboards, and video sessions, while hosting in Fujairah closes the distance to Gulf users and keeps Europe and South Asia within striking range. The right peering must be in place. If your dedicated server is riding on contended links or lacks peering, then the price you pay to close the delay by hosting in-region is almost pointless. To understand whether you have a solid network design, make sure to monitor end-to-end response time before and after cutover and ensure it meets a sub-2-second bar for common journeys.
Balancing Costs and Quality in Fujairah

Keep things straightforward with the following tips:
- Insist on Tier III as a baseline for engineered resilience: Melbicom’s data centers (including Fujairah) all adhere to Tier III specifications and Tier IV in Amsterdam.
- Match the offered hardware to your expected workloads: SSD/NVMe is vital for IO-bound apps, and you must have current-gen cores for CPU-bound services and sufficient RAM for analytics. Melbicom offers a variety of configurations that are ready to deploy, with custom options available.
- Design with low latency as a focus. Start from your users and engineer backwards; make Fujairah your origin with front static assets cached via the CDN and API calls kept local. Lower your p95 latency with stateful services held in the UAE and globally caching the rest.
- Don’t underestimate support: Cheap plans without support mean external incident costs and instability. Melbicom includes free 24/7 support, eliminating hidden future incident support costs.
- Check the fine print and avoid any lock-ins: Pricing and bandwidth terms should be clear. You should also make sure there are options for straightforward upgrades that don’t require replatforming. Avoid anything vague.
Conclusion: Affordable But Reliable
Navigating the value end of the dedicated hosting market in the UAE can be fraught with liability. Sure, there is plenty of choice, but some of these “cheap” offers conceal outdated components, networks that squander, or are housed in facilities that are ill-equipped. The support (if available at no extra cost) is often late to the party, long after the damage is done, and these deals often come with limits that force migrations with the worst possible timing. All of this equates to stalled growth, latency issues, and unacceptable downtime, especially in a region where user expectations are unforgiving. Modern users have high demands regardless of where they are in the world. What you need to focus on when choosing a server is performance, reliability, and the foundations for undisrupted growth.
When budgets are low, you have to spend where it matters the most. By making the facility tier, network, support, and hardware specifications your priorities, you can keep costs in check and protect your revenue and reputation. Melbicom’s Fujairah deployment provides low-latency local performance without the fragility associated with the rock-bottom tier in the UAE. It also puts you in a prime position to scale because we have 19 additional global locations and 50+ CDN points, and Fujairah servers offer up to 20 Gbps per server with round-the-clock support.
Deploy a UAE Dedicated Server Today
Launch a Tier III facility-hosted Fujairah server with up to 20 Gbps bandwidth and 24/7 support in minutes.
Get expert support with your services.
Blog

MongoDB vs. SQL: Choosing the Right Database Hosting
A dozen years ago the NoSQL-versus-relational argument was a winner-takes-all brawl. Reality intervened. By the mid-2020s only 8 % of engineering teams rely solely on NoSQL, while 49 % operate mixed fleets . The question is no longer which model wins but how to balance agility, consistency, and scale—then host the result on reliable infrastructure that never blinks.
This guide compares the two models around four pillars—data model, scaling topology, schema philosophy, and feature convergence—and closes with hosting patterns that exploit Melbicom’s global dedicated-server footprint.
Choose Melbicom— 1,000+ ready-to-go servers — 20 global Tier IV & III data centers — 50+ PoP CDN across 6 continents |
 |
What’s the Difference Between Document and Tabular Models?
Relational tables enforce typed columns, keys, and constraints. Decades of query-planner research let a single SQL statement join 20 tables and stream aggregates in milliseconds. In turn, schema changes require migrations and downtime planning.
Document stores such as MongoDB treat each BSON document as a self-contained record: schemas may differ, nested arrays replace joins, and new fields ship with the next deploy.
| Model | Strengths | Trade-offs |
|---|---|---|
| Tabular (SQL) | ACID, mature JOIN/aggregate engine, static typing | Slower schema evolution; multi-node write scale is complex |
| Document (MongoDB) | Schema agility, high write throughput, hierarchical reads | Joins less efficient; integrity rules shift to application |
Hybrid adoption is now normal: finance ledgers in PostgreSQL; content metadata in MongoDB. 49 % of organizations run at least one SQL and one NoSQL engine —proof that polyglot persistence is the mainstream path.
Sharding vs. Clustering: How Do You Scale MongoDB and SQL?
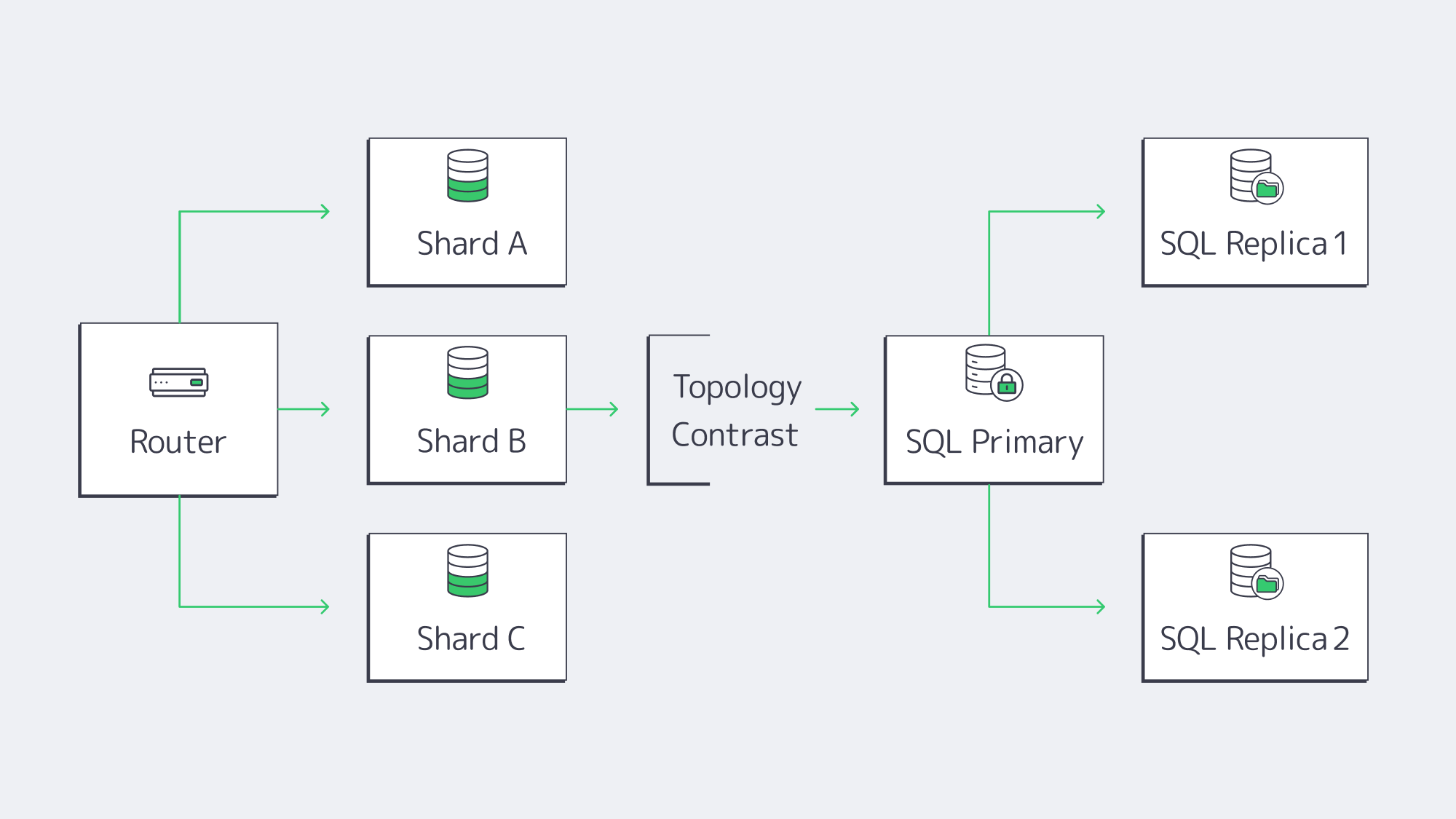
- MongoDB sharding automatically partitions collections by a shard key, balances chunks across servers, and scales writes linearly—petabyte datasets and six-figure TPS are routine. Replica sets add fail-over with a few configuration flags.
- Relational engines historically scaled up (more CPU, RAM, and NVMe). Read replicas handle analytics, and manual partitioning spreads writes. “Distributed SQL” products mimic Mongo-style sharding, but adoption is early.
Topology drives hosting: a sharded MongoDB fleet may span half-a-dozen mid-grade servers; a mission-critical SQL system often lives on one giant node plus synchronous replicas. Cost is context-specific. Three 8-core MongoDB nodes can undercut a 64-core SQL box if licenses are factored in; the reverse is true when SQL Server cores are already owned. Smart DBAs run a quick spreadsheet before committing.
Flexible Schemas vs. ACID: When Should You Prioritize Each?
MongoDB’s schema-on-read lets developers add attributes without running ALTER TABLE, shaving weeks off large-scale migrations. OTTO—one of Europe’s largest e-commerce marketplaces—cut product-catalog refresh times from 12 hrs to 15 mins after adopting MongoDB, yet it may later have spent days cleansing documents that lacked newly required compliance flags. Flexibility, in other words, still demands strong governance.
Relational databases refuse malformed data and guarantee ACID transactions. Financial transfers or inventory debits either complete entirely or roll back—no phantom states .
The gulf has narrowed. MongoDB added multi-document ACID transactions in 4.0 (replica sets) and 4.2 (shards) . Conversely, PostgreSQL, MySQL 8.0, and SQL Server 2022 store and index JSON nearly as fast as native document stores . Architects can now dial flexibility and rigor per collection or table: money flows stay in SQL, polymorphic user data in MongoDB, validation in APIs, and correlation IDs tie the story together.
Convergence Features—Transactions & JSON Everywhere
- Analytics in MongoDB –
$lookup joins, window functions, and time-series buckets narrow the query gap. - SQL JSON – PostgreSQL 15’s
jsonb_path_opsindexes shave 30 % off key-path lookups; SQL Server 2022 builds computed indexes on JSON paths. - Vector & graph – pgvector and MongoDB Atlas Vector Search arrived in 2024 for AI similarity retrieval workloads.
- Consensus replication – Raft algorithms deliver predictable fail-over on either platform.
Selection is therefore less about missing features and more about ergonomics: document stores excel at sparse datasets, relational engines dominate deep joins and ad-hoc analytics at scale today.
Decision Framework for Modern Deployments
| Criterion | Lean Document | Lean Relational |
|---|---|---|
| Data shape | Polymorphic, nested | Highly normalized |
| Query profile | Simple key lookups | Multi-table joins |
| Consistency | Eventual acceptable | Strong required |
| Growth | Horizontal writes | Vertical or distributed-SQL |
| Licensing | SSPL/FOSS | FOSS or $$$ |
| Ops skill | Dev-led JSON | DBA-led SQL |
MongoDB Database Hosting: Why Do Dedicated Servers Matter?

Databases are sensitive to jitter. Multi-tenant clouds hide hypervisors and shared disks that can spike latency 10×. Dedicated hardware restores determinism:
- Local NVMe > 3 GB/s; cloud network volumes may cap at 500 MB/s.
- Full CPU cache means consistent query plans; no stolen cycles.
- Kernel tuning—
nonescheduler, huge pages—requires root, which bare metal provides.
We at Melbicom supply 1,000+ ready-to-go dedicated server configurations across 20 global data centers. MongoDB shards in Paris, SQL replicas in Los Angeles, private backbone in between—24 × 7 support swaps any failed hardware while DBAs sleep.
Cost Dynamics of Dedicated vs Cloud for Database Loads
Storage and I/O remain the stealth budget killers. A sharded MongoDB pipeline that ingests 30 TB of event data every month can still generate $20 k–30 k in cloud I/O fees, while a heavy Microsoft SQL Server instance on a supersized VM can ring up $0.20 per log write once tempdb starts thrashing. By contrast, a fixed-price dedicated server bakes the cost of high-end NVMe into one predictable monthly bill—no metered surprises.
Many architects begin their cost research with the evergreen query “how much does Microsoft SQL Server cost?” and quickly discover that license fees stack on top of cloud charges. Upgrading directly to SQL Server 2022—and running it on Melbicom hardware with all cores properly licensed—often proves cheaper and far safer than maintaining any out-of-support edition.
Separately from databases, Melbicom amplifies savings with 50+ CDN PoPs: static assets stay at the edge—independent of the database path—reducing application egress. For database traffic itself, replicas syncing between Paris and Madrid traverse our private backbone, not the public Internet, keeping replication low-latency and predictable.
Operational Playbooks and Tooling
Bare-metal no longer means hand-crafted scripts. Ansible, Terraform, and Kubernetes bare-metal operators cover day-0 through day-n. Melbicom’s API exposes IPMI and power-cycling endpoints so DevOps can automate reboots; IP block management, image loads, and IP failover can be integrated via customer tooling or handled through support workflows. TLS certs can auto-renew, metrics can ship to Grafana, and RAID rebuilds can alert PagerDuty—all while packets stay inside the data-center copper. You gain private-cloud ergonomics with public-cloud speed—a distributed-cloud operating model.
Hosting Patterns at a Glance
| Pattern | Typical Nodes | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Single Powerful SQL Box | 1 × 32–64 core, 256 GB RAM | High-value OLTP & analytics |
| MongoDB Sharded Cluster | 3 config + N shards, 8–16 core each | Write-heavy, unstructured data |
| Polyglot Mesh | Mix behind 10 GbE | Apps needing both models |
Conclusion—Agility, Consistency, Scale: Pick Two, Host Smart

Modern database engineering is about compromise. MongoDB accelerates development and horizontal growth, while SQL engines guarantee incorruptible state and slice data from every angle. Feature convergence softens extremes, yet each model retains superpowers the other only emulates. The decisive factor is operational: align engine strengths with infrastructure that delivers deterministic performance and transparent economics.
Deploy dedicated servers today
Spin up high-performance dedicated servers worldwide in minutes—no setup fees, no surprises.
Get expert support with your services.
Blog
Dedicated Servers for Buffer-Free Streaming at Scale
Video now dominates the internet—industry estimates put it at more than 80% of all traffic. Audiences expect instant starts, crisp 4K playback, and zero buffering.
That expectation collides with physics and infrastructure: a single marquee live event has already reached 65 million concurrent streams; a mere three seconds of buffering can drive a majority of viewers to abandon a session. Meanwhile, a 4K stream typically requires ~25 Mbps and consumes 7–10 GB per hour. Multiply by thousands—or millions—of viewers and the arithmetic becomes unforgiving.
Choose Melbicom— 1,000+ ready-to-go servers — 20 global Tier IV & III data centers — 50+ PoP CDN across 6 continents |
 |
Choosing the right dedicated server is no longer about generic CPU and a 1 Gbps port. It’s about massive bandwidth headroom, predictable performance under concurrency, CPU/GPU horsepower for real-time encoding, and NVMe storage that feeds the network at line rate. This piece lays out the modern requirements for video streaming hosting, trims legacy considerations to context only, and shows where dedicated infrastructure—paired with a global CDN—gives you both smooth playback and room to scale.
What “Modern” Means for Video Streaming Server Hosting
Four pillars define streaming-ready servers today:
- Network throughput and quality. Think 10/40/100+ Gbps per server. Low-latency routing, strong peering, and non-oversubscribed ports matter as much as raw speed. We at Melbicom operate a global backbone measured in the double-digit terabits and can provision up to 200 Gbps per server where required.
- Compute for encoding/transcoding. HD and especially 4K/AV1 workloads punish CPUs. You’ll want high-core, current-generation processors, plus GPU offload (NVENC/AMF/Quick Sync) when density or latency demands it.
- Fast storage and I/O. NVMe SSDs eliminate seek bottlenecks and sustain multi-gigabyte-per-second reads. Hybrid tiers (NVMe + HDD) can work for large libraries, but hot content belongs on flash.
- Distributed reach via CDN. Even perfect origin servers won’t save a stream if the path to users is long. A CDN with dozens of global POPs puts segments close to the last mile and offloads origin bandwidth. Melbicom’s CDN spans 50+ locations across 36 countries; origins plug in with standard headers, origin-shielding, and tokenization.
Everything else—kernel tuning, congestion control variants, packaging tweaks—adds incremental value only if these pillars are sized correctly.
Dedicated Servers vs. Cloud
Cloud advantages. Fast time-to-first-instance and elasticity are real benefits. If you’re validating a format or riding unpredictable bursts, cloud can bridge the gap.
Cloud trade-offs for streaming. Video is egress-heavy. At $0.05–$0.09/GB in typical cloud egress, 1 PB/month can add $50k–$90k—for bandwidth alone. Multi-tenant “noisy neighbor” effects and hypervisor overhead also introduce variability exactly when you least want it: during peak concurrency.
Dedicated advantages. You get exclusive hardware: full CPU cores, RAM, NICs—and fixed, often unmetered bandwidth. That predictability keeps latency steady as concurrency climbs, and the cost per delivered gigabyte drops as your audience grows. Dedicated servers also give you full-stack control: CPU model, GPU option, NICs, NVMe layout, kernel version, and IO schedulers—all tunable for media workloads.
A pragmatic strategy. Many teams run steady state on dedicated (for performance and cost efficiency) and keep the cloud for edge cases. Melbicom supports this path with 1,000+ ready-to-go configurations across 20 Tier IV & III data centers for rapid provisioning of the right shape at the right place.
Bandwidth First: the Constraint that Makes or Breaks Smooth Playback
Bandwidth is the streaming bottleneck most likely to surface first—and the one that is hardest to paper over with “optimization.” The math is stark:
- 10,000 × 1080p at ~5 Mbps ≈ 50 Gbps sustained.
- 10,000 × 4K at ~20 Mbps ≈ 200 Gbps sustained.
A once-standard 1 Gbps port saturates quickly; it also caps monthly transfer at roughly 324 TB if run flat-out. For modern services, 10 Gbps should be the minimum, with 40/100/200 Gbps used where concurrency or bitrate warrants. The interface is only part of the story; you also need:
- Non-oversubscribed ports. If a “10 Gbps” port is shared, you don’t really have 10 Gbps.
- Good routes and peering. Closer, cleaner paths reduce retransmits and startup delay.
- Redundancy. Dual uplinks and diverse routing keep live streams alive during incidents.
Melbicom’s network pairs high-capacity ports with a multi-Tbps backbone and wide peering to keep loss and jitter low. The result is practical: a streaming origin that can actually push the advertised line-rate—hour after hour.
Compute: CPU and GPU for Real-Time Encoding and Packaging
Software encoders for H.264/H.265 chew through cores; AV1 is even more demanding. Plan for high-core, current-gen CPUs—32, 64, or more physical cores per server for dense live transcode farms—and keep clock speed in mind when single-stream latency matters. As workflows scale, GPU acceleration becomes the difference between “possible” and “operationally efficient.” A single modern NVIDIA card can handle dozens of 1080p or multiple 4K encodes in real time, freeing CPUs for packaging, DRM, timers, and I/O.
A few practical notes when sizing:
- Match encoders to business logic. If you need multiple ladders (360p→4K) per live channel, compute grows linearly. Hardware encoders compress that curve.
- Use the right instruction set. AVX2/AVX-512 helps software encoders; stay on current CPU generations.
- Right-size RAM. 32–64 GB is a baseline for origins and packagers; live transcoders often need more for buffers and queues.
Melbicom offers dedicated systems with CPU-dense footprints and GPU options ready for media workloads. We’ll help you align codec plans, density targets, and cost per channel.
Storage and I/O: NVMe as the Default, Hybrid for Scale
Legacy wisdom held that “video is sequential, HDDs are fine.” That’s only true in the lab. In production, hundreds or thousands of viewers request different segments, skip around, and collide at popular timestamps—turning your disk profile into a random I/O problem that spinning disks handle poorly. Modern origins should treat NVMe SSDs as the default for hot content:
- Throughput. Single NVMe drives sustain 3–7 GB/s reads; arrays scale linearly.
- Latency. Sub-millisecond access dramatically improves time-to-first-byte and reduces startup delay.
- Concurrency. High IOPS keeps per-stream fetches snappy even under heavy fan-out.
For large libraries, pair NVMe (hot tier) with HDD capacity (cold tier). Software caching (filesystem or application-level) keeps the working set on flash, while HDD arrays hold the long tail. A critical sanity check: ensure storage throughput ≥ NIC throughput. A 40 Gbps port fed by a single HDD will never reach line rate; a few NVMes or a wide HDD RAID can. Melbicom offers dedicated servers with NVMe-first storage so your disks never become the limiter for an otherwise capable 10/40/100/200 Gbps network path.
Global Reach, Low Latency: Origins in the Right Places, CDN at the Edge
You cannot fight the speed of light. The farther a user is from your origin, the higher the startup delay and the larger the buffer required to hide jitter. Best practice is twofold:
- Multi-region origins. Place dedicated servers near major exchanges in your key audience regions—e.g., Amsterdam/Frankfurt, Ashburn/New York, Singapore/Tokyo—so CDN origin fetches are short and reliable. Melbicom operates 20 locations worldwide.
- CDN everywhere your users are. A 50+ POP footprint (like Melbicom’s CDN) minimizes last-mile latency. It also shifts the load: the CDN serves most viewer requests, while your origins handle cache fill, authorization, and long tail content.
Routing features—peering with local ISPs, tuned congestion control, and judicious use of anycast or GeoDNS—trim further milliseconds. For live formats (LL-HLS/DASH, WebRTC), these shave enough delay to keep “glass-to-glass” comfortable and consistent.
Concurrency at Scale: Predictable Performance when it Counts
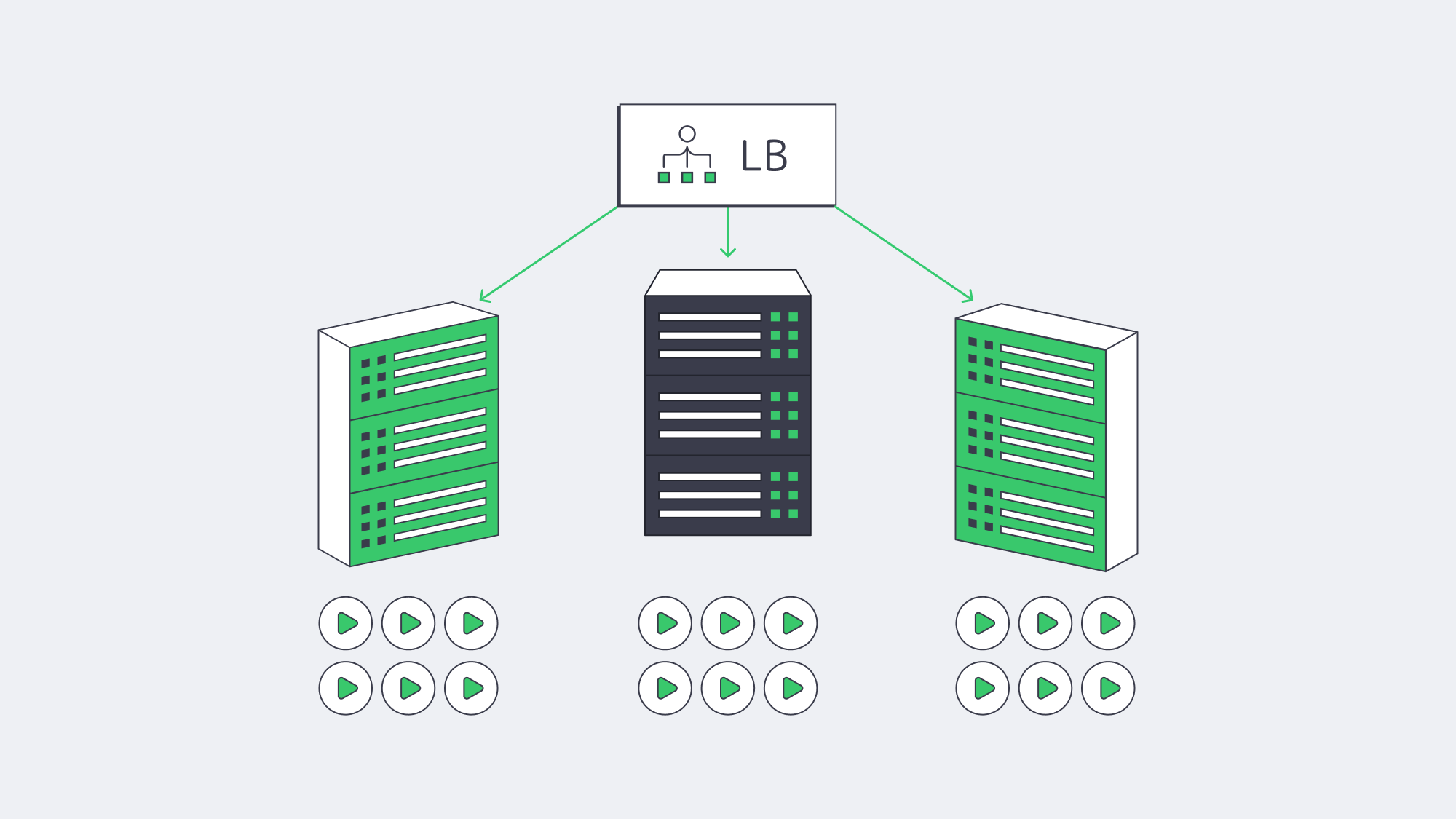
Smooth playback under high concurrency is where dedicated servers repay the decision. Without hypervisor overhead or multi-tenant contention, you get stable CPU budgets per stream, deterministic packet pacing, and no surprise throttles on ports. That stability is the difference between riding out a surge and watching buffer wheels spin. It also simplifies capacity planning:
- Estimate your peak simultaneous viewers and average ladder bitrate.
- Convert to Gbps/headroom targets per origin.
- Add elasticity with either more origins (horizontal scale) or fatter ports (vertical scale).
Because costs are fixed, you can afford to over-provision a bit—buying insurance against viral spikes without incurring runaway per-GB fees.
Future-Proofing: Codecs, Bitrates, Growth
Codec transitions (AV1 today, more to come) and richer formats (HDR, high-FPS, eventually 8K for select use cases) all push bitrate and compute up. Build with headroom:
- Network. Start at 10 Gbps, plan for 40/100/200 Gbps upgrades.
- Compute. Favor CPU families with strong SIMD, and keep a path to GPU-accelerated encoding.
- Storage. Assume NVMe for hot sets; scale horizontally with sharding or caching as libraries grow.
- Placement. Add regions as your audience map changes; test performance regularly.
Melbicom’s model—configurable dedicated servers in 20 locations, an integrated 50+ POP CDN, and high-bandwidth per-server options—lets you extend capacity in step with viewership without re-architecting from scratch.
Practical Checklist for Video Streaming Server Hosting
- Bandwidth & routing. 10 Gbps minimum; verify non-oversubscription and peering quality. Keep an upgrade path to 40/100/200 Gbps.
- CPU/GPU. High-core CPUs for software encodes; GPUs to multiply channels per node and lower per-stream latency.
- Storage. NVMe for hot read paths; hybrid tiers for cost control. Ensure disk can saturate NICs under concurrency.
- CDN. Use it. Pick a footprint that maps to your audience; configure origin shield and sane cache keys for segments.
- Regions. Place origins near user clusters and IXPs; plan failover across regions.
- Costs. Model egress carefully. Dedicated servers with fixed or unmetered bandwidth usually beat per-GB cloud billing at scale.
- Operations. Monitor CPU, NIC, and disk saturation; tune kernel and socket buffers; automate capacity adds before events.
Build for Smooth Playback, Scale for Spikes

The core job of a streaming platform is simple to say and hard to do: start instantly and never stutter. That demands big, clean network pipes, compute engineered for codecs, and NVMe-class I/O—backed by a CDN that puts content within a short RTT of every viewer. Dedicated servers excel here because they deliver predictable performance under concurrency and cost discipline at high egress. When you can guarantee 10/40/100/200 Gbps per origin, encode in real time without jitter, and serve hot segments from flash, viewers feel the difference—especially during peak moments.
If you’re mapping next steps—migrating off the cloud for economics, preparing for a rights-holder’s audience surge, or adopting AV1 at scale—the blueprint is consistent: place origins where they make sense, pair them with a broad CDN, and size network/compute/storage for tomorrow’s ladders, not yesterday’s.
Stream-ready dedicated servers
Deploy high-bandwidth servers in 20 global data centers and start streaming without limits.
Get expert support with your services.
Blog
Choosing Between Object and Block Storage for Your Workloads
Designing a dedicated server environment inevitably runs into a core decision: how to store data. The answer is rarely either/or; it hinges on the workload’s access patterns and long-term trajectory. As global data pushes toward ~180 zettabytes and ~80% of it remains unstructured, the storage fabric must offer both the low-latency precision of block volumes and the scale-out economics of object stores. The sections below compare the two models—architecture, metadata, scalability, consistency, and performance—then map them to best-fit workloads and a practical decision matrix that includes cost, compliance, and hybrid strategies (including S3-compatible gateways).
Choose Melbicom— 1,000+ ready-to-go servers — 20 global Tier IV & III data centers — 50+ PoP CDN across 6 continents |
 |
Object Storage vs. Block Storage: Architectures and Metadata
Block storage exposes a raw device to the OS. Data is split into fixed-size blocks, addressed by offset. The storage layer itself carries no content metadata; meaning and structure come later from the file system or database engine. This minimalism is a feature: it delivers direct, fine-grained control with minimal overhead, ideal for transactional systems and anything expecting POSIX semantics.
Object storage treats data as self-describing objects in a flat address space, each with a unique key and rich, extensible metadata (content type, tags, retention policy, custom attributes, checksums). Access is via HTTP APIs (commonly S3-compatible) rather than a mounted disk. The metadata dimension is decisive: it makes classification, lifecycle policies, and large-scale search practical without bolting on external catalogs.
Implications for dedicated deployments:
- Block volumes (local NVMe/SSD/HDD or SAN-backed LUNs) mount directly to a dedicated server. They favor in-place updates (e.g., 4K rewrites), strict write ordering, and tight OS integration.
- Object stores typically live as a separate service/cluster accessible over the network. They favor write-once/read-many patterns, bulk ingestion, and global distribution, with metadata policies enforcing retention and access.
Object Storage vs. Block Storage: Scalability and Consistency
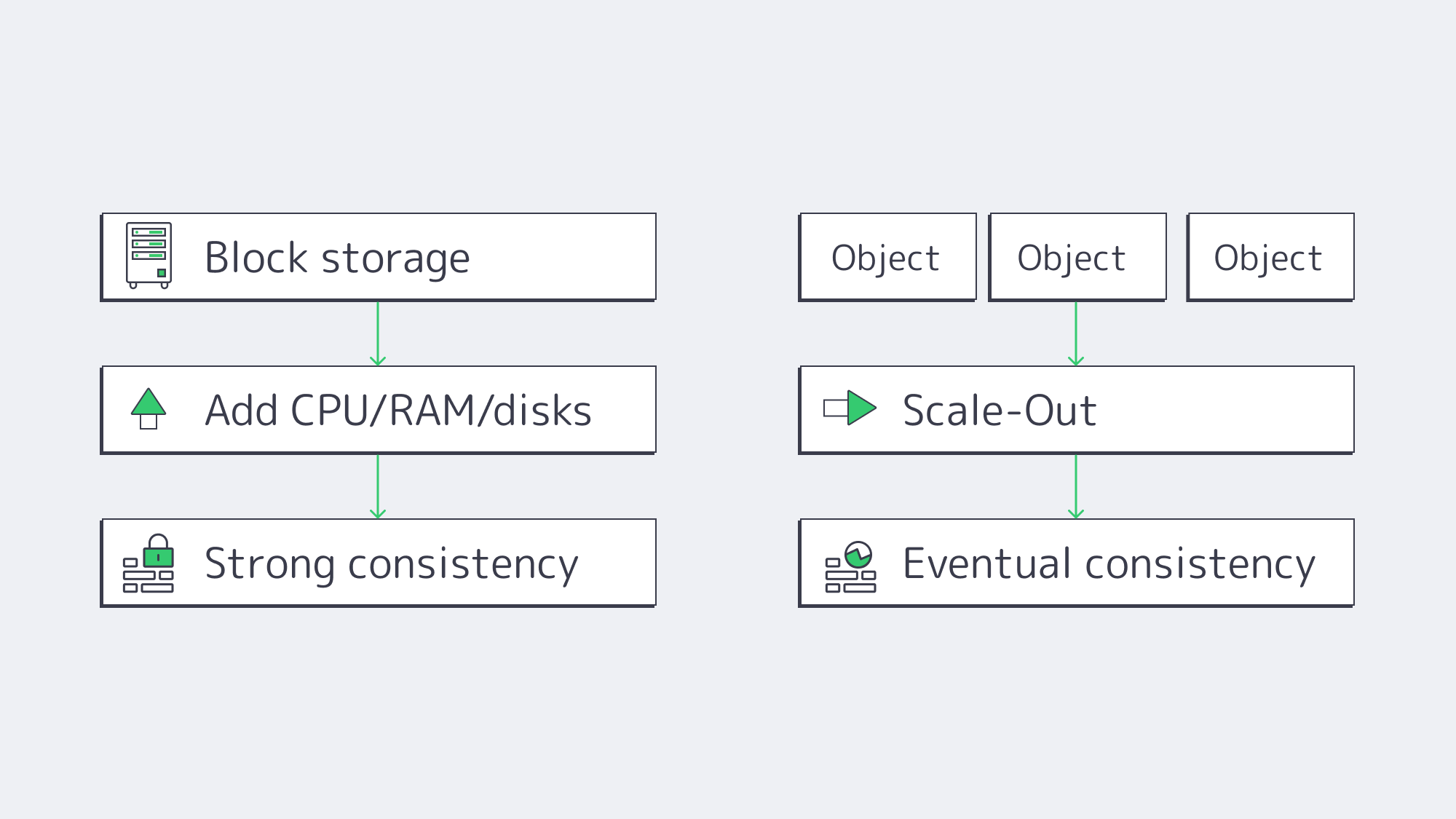
Scalability ceilings. Object storage scales by adding nodes—billions of objects across petabytes is routine thanks to flat namespaces and distribution. Growth is elastic: expand capacity without re-sharding applications. Block storage scales up impressively inside a server or array, but hits practical limits sooner. Beyond a volume/array’s comfort zone, you add LUNs, orchestrate data placement, and manage RAID rebuild domains—operationally heavier at multi-hundred-TB to PB scale.
Durability model. Object stores build durability into the substrate—multi-copy replication or erasure coding across nodes/rooms/regions—with common claims like “eleven nines” of durability. Block storage inherits durability from RAID, mirroring, and backups; robust, but traditionally your responsibility to design and operate.
Consistency. Block storage typically provides strong, immediate consistency at the device boundary; when a write completes, subsequent reads reflect it—non-negotiable for databases and VM block devices. Object systems historically leaned on eventual consistency to scale and remain available across partitions; modern platforms increasingly offer read-after-write or configurable strong consistency, but the default economics still favor eventual consistency for internet-scale workloads. Choose accordingly: strict transactions → block; massive, distributed reads with looser immediacy → object.
Performance profiles: latency, throughput, and IOPS
Latency. Local block storage (especially NVMe) routinely delivers sub-millisecond access. Modern enterprise NVMe drives can sustain read/write latencies well under 1 ms, making tail latency predictable for OLTP and VM workloads. Object access involves network hops and protocol overhead (authentication, HTTP), so small-object first-byte latency lands in the tens of milliseconds. That’s acceptable for archives, analytics batches, and media delivery—not for hot database pages.
IOPS. Block shines on small random I/O. A single NVMe can exceed 1,000,000+ 4K IOPS with enough queue depth and CPU. Filesystems and DB engines exploit this concurrency with fine-grained flush and journaling strategies. Object stores do not optimize for tiny random updates; each PUT/GET is a whole-object operation, better amortized over larger payloads.
Throughput. For large sequential transfers, both models can saturate high-bandwidth links, but object storage often scales aggregate throughput higher by striping a large object across many disks/nodes and reading in parallel. A single NVMe can deliver ~7 GB/s; an object cluster can exceed that for multi-GB objects when the network and clients pipeline aggressively. Rule of thumb: block for latency/IOPS, object for bandwidth at scale.
Two canonical scenarios:
- Relational or NoSQL database on a dedicated server. Needs low-jitter sub-ms access and in-place updates. Keep data/logs on local NVMe or SAN block volumes. Object storage can still serve the ecosystem: WAL/archive logs, snapshots, and cold backups.
- Media delivery or data-lake analytics. Store originals and derived assets as objects; read at high throughput via parallel GETs and push through a CDN. Accept slightly higher start latency for orders-of-magnitude easier fan-out and lifecycle cost controls.
Best-Fit Workloads
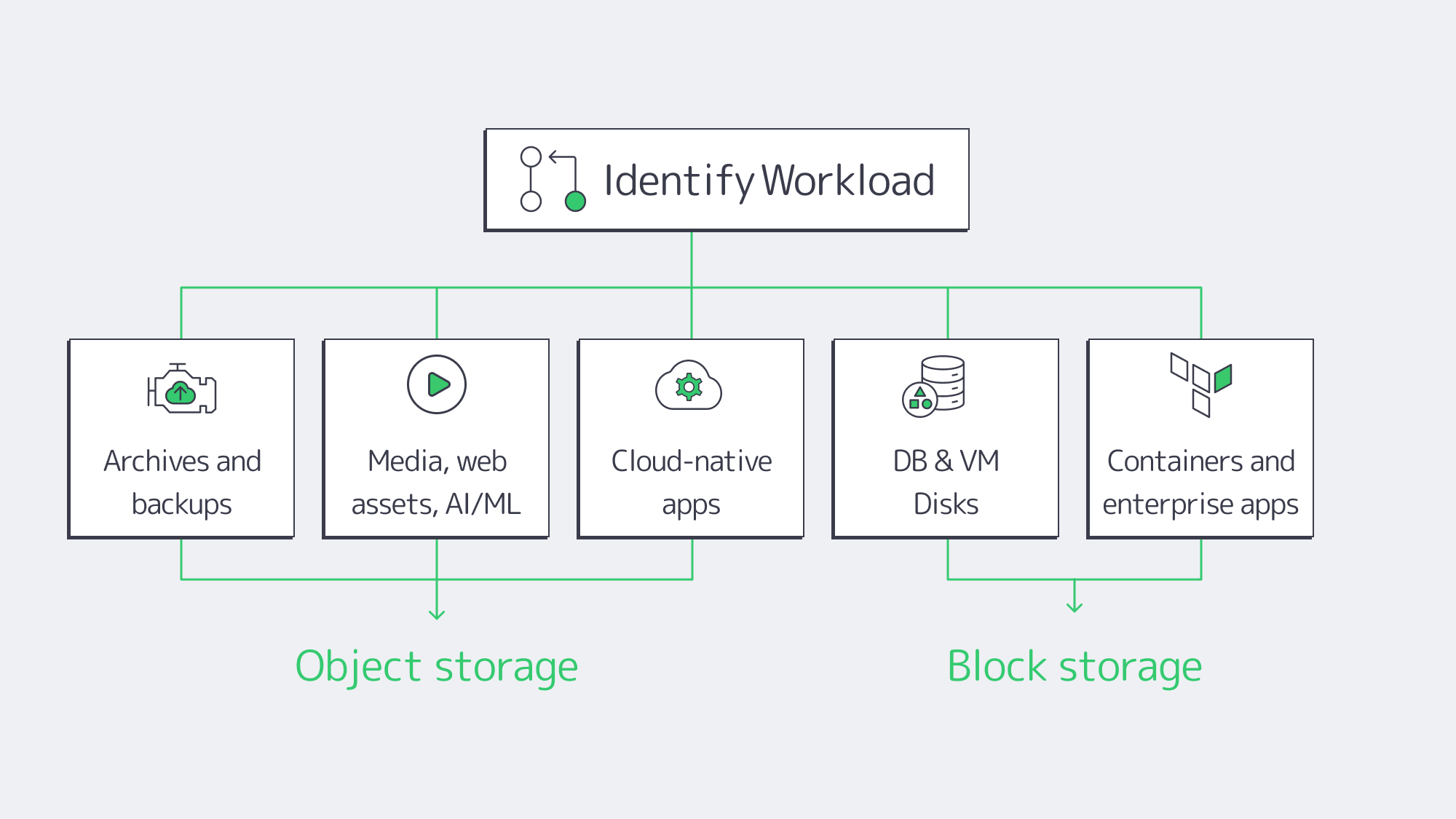
Object storage excels at:
- Archives and backups. Write-once/read-many, versioning, and lifecycle policies enable long-term retention with integrated integrity checks. Cold tiers can cut costs by up to ~80% for infrequently accessed data.
- Media, web assets, AI/analytics inputs. Parallel reads, global accessibility, and rich metadata make it the default backbone for images, video, logs, clickstreams, and ML training corpora.
- Cloud-native apps. Microservices exchange artifacts and user content via S3 APIs; metadata drives governance, and replication underpins cross-site DR.
Block storage is the default for:
- Databases and VM disks. Low-latency, strong consistency, in-place updates. Enterprises routinely keep sub-1 ms latency targets for mission-critical systems.
- Stateful containers and enterprise apps. Persistent volumes, high IOPS scratch capacity, and deterministic flush semantics for ERP/CRM streams, message queues, and build pipelines.
Decision Matrix: Cost, Compliance, Operations, and Hybrid Readiness
Cost. Object storage wins on $/GB at scale, running on commodity nodes with automatic tiering; capacity grows elastically, so less over-provisioning. Block storage commands a higher $/GB (especially NVMe) and often requires provisioning for peak IOPS—wasteful when average IOPS are lower (teams routinely overbuy by factors of ~2–3). Shifting static content and archives off block to object commonly yields ~30% spend reductions; moving render outputs or backups to object while keeping hot scratch on NVMe has shown ~40% performance gains in production pipelines.
Compliance and security. Object storage natively supports WORM (object lock), bucket/object-level ACLs, versioning, and geo-replication—ideal for audit logs, legal holds, and long-term records. Block relies on volume encryption, OS permissions, snapshots, and external backup/replication tools to achieve similar ends.
Operations. Object clusters scale out with minimal re-architecture; add nodes, let the service rebalance, and enforce lifecycle policies centrally. Block requires deliberate capacity and performance planning: RAID level selection, LUN layout, queue tuning, snapshot windows, and database/table partitioning as datasets grow.
Hybrid readiness. S3 has become the lingua franca. S3-compatible gateways can expose object buckets as NFS/SMB to legacy apps or cache writes locally while committing to the object backend—practical for phased migrations. Conversely, NVMe-over-Fabrics pushes block semantics across the network with near-local latency, enabling disaggregated “block pools” for dedicated fleets.
Comparison at a Glance
| Factor | Object Storage | Block Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Distributed service, HTTP (S3) access; flat namespace with object keys. | Device-level volumes to the OS (local or SAN/iSCSI/NVMe-oF). |
| Metadata | Rich, extensible metadata per object; first-class for policy/search. | None at the block layer; context comes from the file system or app. |
| Scalability | Elastic scale-out to billions of objects/petabytes with node adds. | Scales up well but hits volume/array ceilings; add LUNs and manage placement. |
| Durability | Built-in replication/erasure coding; “11 nines” durability claims are common. | Provided by RAID/mirroring/backups you design and operate. |
| Consistency | Eventual by default at internet scale; many platforms offer read-after-write or tunable strong modes. | Strong and immediate at the device boundary; ideal for transactions. |
| Latency | Tens of milliseconds typical for small objects (network + API). | Sub-millisecond on NVMe/SSD is common for small random I/O. |
| Throughput | Excellent for multi-GB transfers via parallel reads across nodes. | Excellent within a server/array; single device ~7 GB/s; scale beyond requires sharding. |
| IOPS | Not optimized for tiny random updates; whole-object PUT/GET. | High IOPS (often 1M+ per NVMe) for 4K random operations. |
| Workloads | Archives, backups, media, data lakes, AI/analytics inputs, cloud-native artifacts. | Databases, VM images, stateful containers, enterprise apps, HPC scratch. |
| Cost/Ops | Lowest $/GB at scale; lifecycle tiering (e.g., cold object tiers) can save ~80% on cold data; simpler growth. | Higher $/GB; over-provisioning for IOPS is common; more hands-on tuning and backup orchestration. |
Hybrid Strategies and the Road Ahead
The architecture that wins is the one that matches storage type to data behavior and keeps migration paths open. A pragmatic pattern:
- Hot tier on block. Keep transactional databases, VM disks, and build/test scratch on local NVMe or shared block volumes. Enforce sub-ms latency and predictable IOPS.
- Warm/cold tiers on object. Move static content, logs, and historical datasets to object buckets with lifecycle policies. Use versioning and object lock to protect backups and audit trails. Cold tiers can trim storage costs by ~80% for rarely accessed data.
- Integrate with S3-compatible gateways. For legacy workflows, front a bucket with NFS/SMB to avoid rewriting applications. For cloud-adjacent analytics, process directly from S3 endpoints without copying back to block.
- Design for convergence. Unified platforms increasingly present file and object on a common backend, and NVMe-oF is bringing near-local block latency over the network. Both trends reduce trade-offs: object becomes faster and more “filesystem-like,” while block becomes more elastic and shareable across dedicated fleets.
In dedicated environments, that translates to: place data where it performs best today, automate its lifecycle to where it costs least tomorrow, and rely on open interfaces (S3, POSIX, NVMe-oF) so you can evolve without re-platforming.
Conclusion: Design for Performance and Scale—Not Either/Or
Object and block storage solve different problems by design. Block gives you deterministic, low-latency control for every 4K update—perfect for databases, VM disks, and stateful services. Object gives you near-limitless scale, integrated durability, and governance—perfect for archives, media, analytics inputs, and cloud-native artifacts. The most resilient dedicated environments blend both: block for hot paths, object for everything that benefits from distribution and lifecycle economics.
If you are planning the next refresh or building net-new, start by inventorying access patterns and consistency. Put strict transactions and small random I/O on block. Put bulk, unstructured, and shared-across-sites data on object with policies for retention, versioning, and tiering. Add S3-compatible gateways where you need to bridge legacy interfaces, and consider NVMe-oF as you centralize high-performance pools. The result is a storage fabric that meets SLAs today and scales gracefully as datasets—and ambitions—grow.
Launch Your Dedicated Server
Choose from 1,000+ configurations and spin up servers with NVMe and 200 Gbps bandwidth in 20 global locations.
Get expert support with your services.
Blog

Future-Proof iGaming with Global Dedicated Server Clusters
iGaming has seen a steep growth curve that is only predicted to continue, with the market’s global value projected to surpass $126 billion within the next few years.
However, despite the demands, scaling has a few caveats. The usage patterns are tricky to calculate with huge spikes in traffic that far exceed daily baselines during major events to contend with, as well as the near-zero tolerance that gamers have for delays. Mere millisecond shifts in latency dramatically affect user behavior, meaning that scalability relies less on procurement factors and more on architectural design.
To keep scalability future-proof, you need a forward-looking roadmap. Today, we will discuss what that actually looks like. To meet the needs of iGaming, with infrastructure on dedicated servers, the emphasis has to be on horizontal clustering and low latency. The server capacity needs to be adequately planned and managed, with automation in place to cater for emerging and chaotic workloads intelligently. So let’s take a look at a scalable blueprint with modular resilience for AI, real-time analytics, and blockchain that works smoothly and efficiently under realistic workloads.
Choose Melbicom— 1,000+ ready-to-go servers — 20 global Tier IV & III data centers — 50+ PoP CDN across 6 continents |
 |
Horizontal Clustering: The Bedrock of Scalable Dedicated Servers for iGaming
Scaling vertically requires ever-larger machines; realistically, it means finite headroom for most. The overprovisioning is often wasteful and creates single points of failure within the infrastructure that lead to longer maintenance windows and result in more downtime. By adding servers in parallel with horizontal clustering, you have a better alternative that intelligently balances traffic without wasting provisions, and failure is treated as a routine event rather than a deadly threat.
Horizontal clustering also allows you to separate concerns into independently scalable pools. For iGaming operations, the separation blueprint of tiers would be the following:
- For Web/API and game servers: Nodes remain as stateless as possible and are routed with L4/L7 load balancers. Game rooms and tables are partitioned through consistent hashing, and game nodes are added to the pool when a tournament starts. This prevents tuning and pushing a single box past its breaking point.
- For the data: Heavy reads are dealt with by blending read replicas, and writes are handled via clustering or sharding. The transaction integrity is protected by distributed SQL or sharded RDBMS patterns, and bet placement, settlement, and odds queries are easily handled regardless of the volume.
- Maintaining a low-latency state and messaging: In-memory caches and message queues help decouple spikes from the database’s critical path.
Operating in clusters boosts throughput and availability because health checks and load balancers can drain a single server should a failure be encountered, while the rest continue working. This means safer rollouts, as new builds can be hosted on a subset of nodes with blue-green deployment or canary setups. With a model that adds nodes to increase headroom, your capacity grows in alignment with growing demand, and there is no need for any redesigning, regardless of whether you need to scale from five thousand to fifty thousand concurrent users at a moment’s notice.
This blueprint is easy to start; Melbicom’s dedicated servers align cleanly. We have more than 1,000 ready-to-go configurations capable of providing up to 200 Gbps per-server bandwidth, which enables you to obtain the right-sizing for the above outlined tiers, as well as have the headroom on hand to expand clusters as and when concurrency climbs.
Lowering Latency and Aligning with Regulatory Requirements
We often think of scaling in terms of “how much,” but “where” is just as important, especially in iGaming, with latency being a key concern. Physical distance equals delay; the longer the distance between a player and your servers, the more latency erodes conversion and churn. Gameplay and in-play betting should be instantaneous for all users, even if those at the table are located as far apart as Madrid, LA, and Singapore at the same time. To provide that globally, multi-regional deployment is vital to your infrastructure.
Design with regional hubs as your focus: Place your active clusters in key geographical regions (e.g., EU, US, APAC). DNS-based global load balancing or anycast can help ensure that a bet placed in Frankfurt resolves to Europe by default, whilst an Atlanta-based one lands in North America. Keep the data local to make compliance easier. Use active-active operation where possible to keep failover seamless and capacity steady.
Free the core cluster via CDN offload: Reduce origin loads and roundtrips by pushing static assets, media, and selected API responses to the edge. The Melbicom CDN spans over 50 locations, ensuring that assets and streams terminate within proximity of the user, freeing up the core cluster and enabling the focus to be on latency-sensitive interactions.
Physical foundational considerations: High-capacity, well-peered networks in fault-tolerant facilities are needed to keep user experiences consistently sub-100 ms. Melbicom operates with a geo-redundant design with data centers in 20 global locations that ensure rapid transactions and recovery. Our data centers have redundant power and diverse network paths, preventing regional incidents from causing any prolonged downtime.
The big payoff of operating with regional hubs is that regional traffic peaks locally; spillover is caught by neighbors; for example, surges from the Champions League are handled by European clusters, the Americas absorb spikes caused by the NFL, while APAC handles weekend traffic.
Handling Surges Seamlessly with Automation and Server Capacity Planning
The iGaming market moves rapidly, and the supply and demand for server capacity are unpredictable, making it tough to keep up with through manual scaling. To keep ahead, automation and server capacity planning are vital; if not, you run the risk of last-minute scrambles that spoil UX.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC). You can smoothly expand clusters in planned windows to cover predictable surges with a ready-to-deploy inventory by provisioning and reimaging servers using code (Terraform/Ansible). At the same time, standardized images across nodes prevent configuration drift.
Elastic orchestration. Although physical servers don’t “pop” instantly, near-instant service-level elasticity can be achieved on dedicated hardware, comparable to cloud operation, by packaging services into containers, scheduling with a cluster manager, and autoscaling horizontal pods on CPU/memory/queue depth.
Autoscale through blending predictive and reactive triggers:
- Schedule calendar-based rollouts, derbies, tourneys, and promotional campaigns.
- Set reactive triggers such as thresholds on error budgets, P95 latency, specific queue lengths, or cache hit rates.
- Avoid idle waste by automating graceful cooldowns when surges recede.
Close the loop with health checks and continuous load testing to analyze previous peak behavior. This ensures that traffic is drained away from unhealthy instances and restart through automation, and that pipelines roll forward and back automatically.
Through this method, you remain cost-aware at baseline, ruthless with headroom, and far more efficient than manually possible.
Build to Fail Safely with Modular, Resilient Architecture as a Backbone

As well as the hardware considerations, you have software architecture to think about if you truly want your scalability to remain future-proof. The benefits of a modular system as a backbone are: localized failure, rapid feature integration, and the ability to scale components independently.
Microservices and event-driven flows: Break down the individual platform services such as identity, wallet, risk, odds, settlement, game sessions, chat, bonus, and analytics. Use APIs and streams for communication. Publish event-driven actions such as “bet placed,” “odds updated,” or “game finished” to a durable bus; adding a fraud model or a loyalty engine is a plug-in, not a rewrite.
Isolation and fallbacks: Ensure that each microservice is isolated so as not to cause collapse should a failure arise, and have a fallback in place for each. Some examples would be: If chat features start to slow, degrade them, but allow bets to proceed. If personalization times out, revert to default settings. Putting these patterns in place for resilience helps counter timeouts, reducing degradation from cascading partial outages.
Redundancy should be throughout: Use primary/replica or clustered databases with automatic failover to make sure that no single data node, cache, or gateway is a lynchpin. Keep multiple instances of all stateless services and run hot spares for critical paths. Site-level incidents can be handled via active-active regions where possible, and if not, at the very least, hot standbys.
Harden your architecture design through regular testing: Run chaos drills in staging and practice region evacuation and database failover. That way, you can make sure that load balancers stay true to health checks and get your rollback paths as predictable as possible.
Working this way protects revenue, preventing outages during the Super Bowl, and accelerates delivery, giving your teams the confidence to deploy changes.
AI, Real-Time Analytics, and Blockchain Readiness
As you scale and integrate other features, the emerging workloads can cause upheaval. The best practice is to architect ahead of yourself a system that is ready for anything.
For AI and real-time analytics operations that rely on streaming events and compute-intensive pipelines such as recommendation engines, risk models, anomaly detection, and dynamic odds, the transactional paths need to be kept as clean as possible (write bet → ack). The events can then be mirrored to analytics clusters and engineered. Through model scoring, you can work out where to add a GPU dedicated server to bolster and accelerate alongside adjacent data streams. By treating analytics stacks as separate but first-class tenants, they can be scaled independently without starving bet paths, which also allows for experimentation, because models can be rolled forward without risking core stability.
You should track P95 latency for real-time operational analytics, such as a dashboard for bet placement, queue times for settlement, cache hit ratios, and regional error budgets, to make sure automation responds rapidly to line breaks or traffic shifts.
Crypto wallets and provably fair gaming, which rely on Blockchain , can write very slowly or be transiently unavailable. The solution is to have their gateways isolated behind queues to prevent stalling when awaiting confirmations. Integrate modularly to keep the core platform running smoothly regardless of any external network hiccups. Remember that fast NVMe stateful nodes require high-bandwidth links to sync heavy chains and state snapshots. At Melbicom, we offer uplinks with up to 200 Gbps per server.
Modularity also helps cover new interaction patterns. VR/AR tables, large-scale PvP pools, and social gameplay can all cause unpredictable surges. To cope, you need architecture that lets you place specialty services in regional hubs and add edge offload via CDN. WebSocket, HTTP/2, and other protocols should be tuned for connection at scale.
This architecture is more pragmatic in terms of costing, with a disciplined baseline (e.g., 60–70% utilization) and planned surge capacity, you evade overbuild and panic-buy cycles, just use the right-sized node types per tier and don’t use GPUs where CPUs suffice.
Further tips: to ensure rightsizing and detect anomalies early, you can leverage unified tracing, analyzing metrics, and logs across tiers. Tie SLOs such as bet latency and odds freshness to automated actions and keep personal and wagering data in-region by default. That way, you replicate summaries rather than raw PII across borders, satisfying auditors.
Growth Pattern Reference
You can use the following summary as a reference for your iGaming architecture blueprint:
- Operate horizontally from the get-go by deploying multiple web/API and game nodes with load balancers to help keep nodes as stateless as possible.
- Introduce caches and queues and utilize clustered databases with read replicas to help decouple the data path.
- Launch globally early by placing small but real clusters in your two most important regions, route by proximity through global load balancing, and keep the user data local to simplify compliance.
- Build IaC, golden images, and orchestrate your deployments with automation to scale. Predict known events and employ reactive triggers to allow for any unexpected surges.
- Ensure each tier has redundancy, test failovers, and add graceful degradation paths to protect against failure.
- Keep bet paths clean by supporting the core with analytics and AI to stream events and score models out-of-band, returning only the necessary signals.
- Observe to iterate, trim any waste, move bottlenecks, and use the data to inform the next scale-up.
Be sure to choose facilities and networks that won’t result in any bottlenecks. Melbicom’s dedicated servers are housed in Tier IV & III sites across 20 global locations. The infrastructure is engineered for redundancy, and each server provides connectivity up to 200 Gbps, meaning sudden spikes won’t saturate the network.
Building with Sustained Global Performance as a Focus
If you want to ensure that your iGaming scaling capabilities are future-proof in iGaming, then you need a disciplined architecture that is built to work in parallel and focused on proximity and automation. You can give your capacity more elasticity and resilience through horizontal clustering, which, paired with automation and server capacity planning, helps you cope with the chaotic traffic expectations. Global deployment ensures low latency and fairness, helping to satisfy regulators, and failure containment is easier to deal with thanks to the modular nature of the blueprint. These architectural design choices work hand in hand to ensure your scaling is steady and smooth rather than episodic and make engineering for iGaming predictable despite the challenges that event days and release cycles can otherwise cause.
The result is a platform that is architecturally strong and resilient as opposed to simply bigger, which means surges are easily absorbed, features launch faster, and the future integration of AI, analytics, and blockchain won’t cause any disruptions. Reaping the rewards of this architectural blueprint requires dedicated servers in global locations that are clustered, observable, and automated from the bootloader up to provide the perfect iGaming infrastructure.
Launch Your iGaming Servers Today
Choose from 1,000+ high-bandwidth dedicated servers across 20 global data centers and scale your platform without limits.
Get expert support with your services.
Blog
Boosting Affiliate Conversions with High-Performance Dedicated Servers
Affiliate campaigns are hyper-sensitive to latency. The pages that can be opened within two seconds and those that take three seconds or more may represent the profit and loss difference. Google reports show that the probability of bounce increases by 32% as load time moves from 1s to 3s, and more than 50 percent of mobile visitors leave a page in case of a delay of more than 3 seconds. BigCommerce sums it up simply: a one-second delay has been shown to result in a 7% loss in conversions. Affiliates working on a per-click basis, of course, will translate those percentages into margin.
Modern infrastructure bridges that gap. The fastest deployments are those which combine NVMe storage, multi-core CPUs with high amounts of RAM, and optimized high-throughput networks so that time to first byte is short and page rendering is never interrupted, even in the event of a campaign spike. This is also where performance-tuned dedicated servers pay off, because they can deliver long-term throughput and consistent latency under actual load, not just in lab tests.
Choose Melbicom— 1,000+ ready-to-go servers — 20 global Tier IV & III data centers — 50+ PoP CDN across 6 continents |
 |
How Dedicated Servers Help Affiliate Marketing to Convert More Clicks
The 2025–26-class hardware and networks do not offer incremental improvements; they are architectural. NVMe on PCIe 4/5 takes the I/O bottlenecks that once made dynamic pages “feel” slow away. NVMe drives will routinely achieve multi-GB/s sequential reads and writes (5,000 MB/s and higher in typical settings), whereas SATA remains capped at 600 MB/s—a limit that is easily saturated under concurrent requests. On the CPU front, dozens of physical cores and high-speed DDR4/DDR5 RAM enable servers to render templates, execute tracking/attribution logic and serve API requests in parallel without spiking tail latency. On the network, the bandwidth-intensive sites are based on high-capacity, dedicated 1–200 Gbps ports, intelligent peering, and global distribution mechanisms that ensure tight p95/p99 response times even when audiences are far-flung across regions.
In the browser: The HTML renders more quickly, the render-blocking assets come sooner, and an overworked origin does not block the main thread. Users are exposed to content earlier, engage earlier, and leave less often, which is the exact direction toward increased conversion rates. This cumulative effect is enormous: BBC reported that every extra second of load time costs them another 10 percent of users—an object lesson on how small mistakes end up building to significant losses.

NVMe dedicated servers for low latency
The advantage of NVMe is not that it offers high headline throughput, it is that it can provide low latency, high queue depth I/O that can keep dynamic sites responsive when under concurrency.
Consider an affiliate landing page that accesses a geo database, and then retrieves creative variants along with recording a click-ID, all before the content is painted above-the-fold. NVMe reduces the wait times of the reads and writes to microseconds, as opposed to milliseconds, across the request pipeline. The end result is a reduced TTFB, a reduced LCP, and a greater likelihood that the user sees and responds to the CTA.
CPA network dedicated hosting
There is a different but related issue facing networks and platforms: high rates of redirects, attribution and postbacks are required 24/7.
A delay in the tracking hop frustrates the user even before they can see the merchant page. Dedicated servers with high numbers of cores and memory can absorb bursty redirect traffic and high-capacity NICs ensure that traffic does not queue on the wire. Keeping tracking latency minimal preserves conversion probability across all offers and geos; it also preserves trust in reported numbers, which is critical when affiliates bid hourly.
Minimize the time it takes to load an affiliate landing page (infrastructure first)
Front-end minification is useful but infrastructure can frequently be the quickest win in affiliate land.
- Move origins closer to demand and cache as much as you can at the edge. A world-wide CDN reduces distances and round-trips; static content is served by edge nodes leaving origin CPU to concentrate on dynamic tasks.
- Right-size compute at the peaks, not averages. Ample headroom avoids CPU-bound stalls that slow down p95 latency in the times that matter the most (e.g., email drop, social virality).
- Employ new routing and protocols. Consolidated connections (HTTP/2/3), intelligent peering, and anycast DNS eliminate much handshaking overhead and path variability, which is often a silent cause of mystery seconds.
A quick comparison
| Lever | Modern capability (examples) | Conversion-side effect |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | NVMe on PCIe 4/5 exceeds 5,000 MB/s; SATA is limited to ~600 MB/s | Lower TTFB and faster DB-backed renders improve completion of key funnel steps. |
| Compute | 24–64+ cores with fast DDR4/DDR5 and generous caches | Handles concurrency during spikes; stable time-to-interactive. |
| Network & Edge | Dedicated 10–200 Gbps ports, global CDN with 50+ nodes | Shorter paths and higher throughput reduce bounce and keep users on page. |
Scaling Strategies for Peak Campaigns (without Slowing Down)
Outstanding campaigns produce their own form of DDoS traffic. The playbook scales without compromising the latency per request.
Vertical headroom + horizontal scale. Start with servers with a margin (CPU, RAM, and NIC bandwidth) so your initial server configuration will not be slow at 5x baseline. Then add two replicas behind a load balancer to handle the next order of magnitude. With dedicated hardware, the environment is predictable—no noisy neighbors, consistent NUMA layout, and high port speeds.
Fast capacity activation. The historical objection to dedicated servers — slow provisioning — is no longer valid. For example, Melbicom pre-stages 1,000+ ready dedicated server configurations and typically brings servers online in about two hours, so additional capacity is in place when it’s needed during scheduled bursts or surprise viral moments.
Keep packets flowing. Spikes will tend to cause the bottleneck to be the NIC rather than the disk. Melbicom offers data center services with bandwidth up to 200 Gbps per server — useful when low-risk, high-throughput delivery is important to scheduled launches.
Push static to the edge. At Melbicom we couple origin servers with our own CDN across 50+ points of presence. Campaign materials (images, CSS, JS, video clips) sit on the edge, with the origin being concentrated primarily on dynamic processing such as personalization and tracking. This maintains your p95 and p99 times consistent as the number of concurrent sessions increase.
Global placement. Latency increases with distance; about 10 ms of round-trip time is added to each ~1,000 km. Melbicom has 20 international locations, so you can anchor origins close to traffic you are actually purchasing, and replicate into secondary regions as campaigns scale.
Operational preparedness. The soft side is also important: when you need to scale due to the results of load tests, the response time of the support team will determine how fast you will be able to do it. Melbicom offers 24/7 technical support at no charge to teams and our control panel allows teams to modify capacity with ease.
Why a Good Enough Shared Hosting Environment is not Good Enough
Shared machines and undersized VMs used to be the first point of call, but are doomed to fail at scale due to resource contention and unpredictable latency. A neighboring tenant backing up or a burst of noisy processes can add hundreds of milliseconds of unpredictability to your requests — just when you launch a high-spend campaign. Modern dedicated environments remove that variability by providing you with the entire CPU, memory channels, disk bus, and NIC — there is no contention or surprise. What a decade of affiliate traffic has taught us is this: when you need the conversions, you pay the price for infrastructure that is only ‘good enough’.
Affiliates Implementation Checklist

- Extend stateful workloads to NVMe-based dedicated origins. Prioritize renderers, session stores and databases.
- Place origin servers close to users and front all static content with a CDN.
- Plan on headroom (CPU, RAM, bandwidth) so your p95 does not drift during peak.
- Perform a load test preflight and maintain an expansion path (pre-approved configs, DNS/balancer rules, warm replicas). Melbicom’s 1,000+ ready configs and 2-hour activation make this a realistic standard practice.
- Metrics that count: TTFB, LCP and conversion rate by geo/ISP. Correlate latency to abandonment and adjust capacity based on it.
Milliseconds to Money: the Server Infrastructure Benefit

Conversion arithmetic is merciless. Every second of delay eats a part of sales; every millisecond of saved time provides a padding to ROI. The most powerful lever available to an affiliate is the performance envelope of its origin — how fast it can accept connections, read off storage, render dynamic content, and push bytes over the wire at peak. NVMe storage eliminates I/O stalls; high-performance CPUs and RAM can absorb concurrency without the latency whiplash; high-speed, global access ports eliminate costly, round-trip delays. That combination can convert paid clicks into engaged sessions and engaged sessions into revenue even when there is a surge in traffic. It is straightforward, the data speaks: the fewer seconds, the fewer bounces, the more conversions.
Deploy High-Performance Servers
Choose from over 1,000 ready-to-deploy dedicated server configurations and launch in as little as two hours.