Author: admin
Blog
Building a Resilient Multi‑Layer Backup Strategy
Almost all modern businesses rely on data, which can potentially put their finances and reputations on the line. Catastrophic data loss is a real threat for organizations of all sizes.
Ransomware often targets this data, and the methods being used today by cybercriminals are becoming increasingly sophisticated.
Whether it is hardware failure, human error, or an internal breach from a third party, modern server backup solutions can help provide multi‑layered resilience.
These solutions have also come a long way in an effort to counter cybercriminal refinements and now go way beyond nightly tape rotations.
Modern methods embrace automation and restore faster than ever before, helping IT managers guarantee business continuity, compliance, and ransomware resilience, preventing downtime.
Backup Strategy Evolution: From Single‑Copy to Multi‑Tier
The previous standard was once single‑copy or tape‑only backups; however, they each run risks. Recovery is too slow, and single backup sets destroyed or infected mean permanent data loss.
While tapes are better for long‑term archiving, modern threats require more advanced solutions. A combination of multiple copies and periodic snapshots can help combat these threats, especially when coupled with off‑site replication.
Redundancy, immutability, recovery speed, automation, and security are all key aspects. The table below compares legacy methods with modern solutions:
| Aspect | Legacy Methods (Single‑Copy/Tape) | Modern Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Redundancy | Single backup, stored on‑site or off‑site | Multiple copies across diverse locations (cloud, multiple data centers) |
| Immutability | No safeguard against malicious encryption | Immutable snapshots prevent alteration. |
| Recovery Speed | Slow, manual tape retrieval and system rebuild | Ultra‑fast, granular restore of files, volumes, or entire servers in minutes |
| Automation | Mostly manual, with the risk of human error | Policy‑based orchestration to automate schedules and replication |
| Security | Vulnerable to mishandling, theft, or environmental damage | Air‑gapped object storage plus encryption, access controls, and multi‑cloud redundancy |
Organizations are obligated to adhere to regulatory compliance, and when faced with ransomware, if something goes wrong, ultimately, critical data needs to be restored without delay.
Ransomware Resilience: Data Immutability
Modern ransomware attacks often target backup repositories, encrypting or deleting the data to force payments.
A great workaround is immutable snapshots; these snapshots lock the backup data for a set period of time, ensuring it can’t be changed in any way or erased by anyone, regardless of their privileges.
These immutable snapshots are “write once, read many,” meaning that if a malware infection strikes at midnight, a snapshot taken at 11:59 PM remains uncompromised.
Additionally, these backups are bolstered via multi‑layer replication across separate clouds or sites to prevent single‑point failure. If one data center backup is compromised, there is another that remains unaffected.
The replication tasks are swift thanks to high‑speed infrastructure and are monitored to identify any unusual activity. Any backup deletions or file encryption spikes are reported through automated alerts, helping to further protect against ransomware.
How Multi‑Location Replication Ensures Business Continuity
If a single site is compromised through failures or attacks, the data must remain recoverable. Major outages and regional disasters can be covered with multi‑cloud and geo‑redundancy to keep backups safe.
With a local backup, you have the ability to restore rapidly, but you shouldn’t put all of your eggs into one basket. By distributing backups with geographic separation, such as a second copy in a data center in another region or an alternate cloud platform, you avoid this pitfall.
With the right implementation, you can restore vital services properly, such as key business systems and line‑of‑business applications, keeping you protected against hardware failures and cyberattacks while adhering to Recovery Time Objectives (RTOs).
The more diverse and concurrent your backups are, the better your IT department can meet these RTOs.
Another strong method organizations often employ to ensure a fallback copy is always available is the “3‑2‑1‑1‑0” rule. That is to say, they have three copies, in two distinct forms of media, with one kept off‑site, one immutable, and zero errors.
Minimizing Downtime with Ultra‑Fast Granular Restores
While multiple secure backups are key, they are only half of the solution. Regardless of the lengths you go to back up and store data, flexibility and speedy recovery are required for these efforts to succeed.
Organizations must be capable of recovering data without rolling back the entire server, which is where granular recovery comes into play. Downtime can be reduced by restoring only what’s needed, be it a single database table or mailbox. That way, systems remain operational throughout restoration.
If the platform allows, you can also boot the server directly from the backup repository for instant recovery. This helps keep downtime to a minimum and means that you can still operate despite a failure on a server hosting critical services by copying data to production hardware.
With granular recovery and instant recovery, organizations can easily address regulatory demands and maintain business continuity.
Using Air‑Gapped Object Storage as a Final Defense
Live environments can still be devastated by a sophisticated attack despite a strong multi‑layered approach to securing data servers. The same can be said for connected backups, especially when it comes to insider threats. The solution is keeping isolated copies off‑network, otherwise known as air‑gapped backups, much like traditional tape stored offsite once did.
The modern approach differs slightly, elevating the level of protection using offline dormant copies on disconnected arrays or object storage. They only connect for a short window to perform scheduled replication, during which the physical or logically unreachable data cannot be altered. If data is breached, then the dormant copy acts as a final defense, becoming a vital lifeline.
Policy‑Based Automation as a Strong Operational Foundation
Manual backup management is error‑prone. With policy‑based orchestration, IT can streamline backup management processes by defining a schedule and setting retention and replication rules. This rules out the errors that manual backup is prone to.
Once IT has defined backup policies, the system automatically applies them across servers, clouds, and storage tiers, keeping everything consistent no matter the scale of operations.
Servers with “production” tags can be backed up hourly and replicated offsite with 2‑week immutability locks by admins without the need for continual human intervention. Scheduled test restores can also be automated on many platforms to simulate recovery under real conditions, saving time, reducing risks, and demonstrating proof of recoverability for regulatory requirements.
How Modern Server Backup Systems Support Compliance
Reliable data protection and recovery are demanded by HIPAA and GDPR. Article 32 of GDPR, for example, states that personal data must be recoverable in the event of any incident. This is also the case for finance (SOX) and payments (PCI‑DSS).
Modern server backup solutions help organizations to fulfil mandates and duties by enabling encrypted backups and off‑site redundancy failsafes. Immutability ensures the integrity of the data, as does air‑gapping, and having restore tests documented to hand is beneficial for audits.
Through automation, scheduled backups can help meet retention rules, such as retaining monthly copies for seven years, as you have easy access to historical snapshots. These automated backups satisfy legal obligations and are a reassuring trust factor for customers.
Technical Infrastructure: Laying the Foundations of a Robust Backup Plan
A robust backup plan rests upon solid technical infrastructure. To make sure that replication requirements are efficient, high‑bandwidth links (10, 40, 100 Gbps or more) and an abundance of power and cooling are needed. Without redundant power, continuous uptime is not achievable. To meet these requirements, you need to consider tier III/IV data centers provided by those offering global locations for true geographical redundancy.
Melbicom has a worldwide data center presence in over 20 locations, operating with up to 200 Gbps server connections for rapid backup transfers. Melbicom enables data replication in different regions, with reduced latency, helping organizations comply with data sovereignty laws. We have more than 1,000 ready‑to‑go dedicated server configurations, meaning you can scale to match demands, and should an issue arise, Melbicom provides 24/7 support.
How to Implement a Server Backup Solution that is Future‑Proof
Backup architecture needs to be constructed strategically. With the following technologies applied, you have a solid server backup solution to withstand the future:
- Lock data through the use of Immutable Snapshots to prevent tampering.
- Spread data across multiple clouds and sites with Multi‑Cloud Replication.
- Minimize downtime by performing a Granular Restore and recovering only what is necessary.
- Keep an offline failsafe using Air‑Gapped Storage for worst‑case scenarios.
- Automate schedules, retention, and verification ops with Policy‑Based Orchestration.
Remember that live environments need regular testing to verify they are running smoothly and that you will be protected should the worst occur. Test with real and simulated restoration to make sure backups remain valid over time, and be sure to encrypt in transit and at rest with strict access controls.
Conclusion: Always‑On Data Protection on the Horizon
Forgotten single‑copy tapes, modern hardware, and evolving cybercrime methods require modern multi‑level automated solutions.
To thwart today’s ransomware, prevent insider threats, and cope with rigorous regulatory audits, immutable snapshots, multi‑cloud replication, granular restores, and air‑gapped storage are needed.
Leveraging these technologies collectively with solid technological infrastructure is the only way to combat modern‑day threats to business‑critical data.
Get Reliable Backup‑Ready Servers
Deploy a dedicated server configured for rapid, secure backups and 24/7 expert support—available in 20+ global data centers.
We are always on duty and ready to assist!
Blog
Reducing Latency and Enhancing Security with Dedicated Server Hosting
Modern digital services are pushing boundaries on speed and safety. Performance-critical platforms—whether running real-time transactions or delivering live content—demand ultra-low latency and airtight security. Even a few extra milliseconds or a minor breach can lead to major losses. In this environment, single-tenant dedicated server hosting stands out for providing both high performance and robust protection. Below, we examine how hosting on a dedicated server addresses these challenges better than multi-tenant setups.
Dedicated Servers vs. Shared Environments: Beyond the “Noisy Neighbor”
In shared or virtualized environments, multiple tenants operate on the same physical hardware, often leading to the “noisy neighbor” issue: resource contention causes performance dips or latency spikes. Virtual machines (VMs) also add a hypervisor layer between the application and hardware, introducing extra overhead. Meanwhile, dedicated servers deliver complete hardware ownership—no risk of interference from other tenants and zero virtualization overhead. This single-tenant approach results in more predictable performance and simpler security management.
| Key Aspect | Dedicated Server (Single-Tenant) | Shared/Virtualized (Multi-Tenant) |
|---|---|---|
| Resource Isolation | 100% yours, no “noisy neighbors” | Resource contention from neighbors |
| Latency & Performance | Bare-metal speed, no hypervisor overhead | Added overhead from shared hypervisor |
| Security | Physical isolation, custom firewalls | Potential cross-VM exploits |
In some workloads, virtualization does have benefits like easy scaling. Yet for consistent performance and stronger security, dedicated hosting remains unmatched. As multi-tenant clouds grow, businesses that need predictable speed and safety at scale have rediscovered the value of dedicated server.
Sub-10 ms Response Times: How Dedicated Servers Excel in Low-Latency
In latency-sensitive operations, every millisecond counts. Network performance depends on distance, hop count, and how your infrastructure connects to end-users. Dedicated hosting makes it possible to carefully select data center locations—keeping servers near major population centers or key exchange points to achieve sub-10 ms latencies for local users. At scale, those milliseconds translate into smoother user experiences and a measurable competitive advantage.
For example, in electronic trading, a 1 ms improvement can be worth millions to a brokerage firm. While not every platform deals with trades, the same principle applies to anything that needs real-time interaction. A single-tenant server can integrate faster network interface cards and custom kernel drivers, enabling latencies measured in microseconds rather than the tens of milliseconds common in shared environments.
Most important, a dedicated environment ensures consistent latency since you’re not competing for network capacity with other clients. Melbicom has 20 PoP in Europe, Asia, Africa, and Americas, including a Tier IV facility in Amsterdam with excellent European connectivity. By placing servers strategically across these locations, you can slice response times to single-digit milliseconds for local traffic.
Custom Firewall, Private Networking, and Hardware Root-of-Trust
The Power of Custom Firewalls
In multi-tenant setups, firewall configurations are often limited or standardized to accommodate all users. With a single-tenant dedicated server, you can deploy custom firewall appliances or software, implementing fine-grained rules. This flexibility becomes crucial in mission-critical applications, where each port and protocol demands careful oversight. Dedicated hardware also lets you segment traffic on private VLANs, isolating back-end services from the public internet.
Private Networking for Latency and Security
Another hallmark of dedicated infrastructure is private internal networking—ideal for workloads that involve communication among multiple servers. Instead of routing traffic through external networks, you can use private links that reduce latency and diminish exposure to outside threats. Melbicom offers private networking capabilities so our customers can keep sensitive data flows entirely off the public internet. And with dedicated server hosting, bandwidth can reach up to 200 Gbps per machine, ensuring that large-scale data transfers or intense workloads operate smoothly.
Hardware Root-of-Trust: Effectively Fighting Firmware-Level Attacks
Firmware-level attacks are on the rise, with attackers targeting motherboards, baseboard management controllers, and BIOS code. One powerful defense is a hardware root-of-trust: a secure chip (such as a Trusted Platform Module, or TPM) that verifies server firmware at boot-time. Research from the Trusted Computing Group underscores TPM’s effectiveness at preventing low-level compromises. In a shared virtual environment, you might not have direct access to these safeguards. In a dedicated server, you control secure boot settings and can verify firmware integrity before your OS even starts.
Defending Against Modern Threats
Cyber threats have spiked in frequency and intensity. Cloud infrastructures blocked 21 million DDoS attacks last year, an increase of more than 50% over the previous period. While multi-tenant providers do offer layered defenses, sharing the underlying environment can mean broader attack surfaces. Dedicated servers by nature limit those surfaces. You have exclusive use of the CPU, storage, and network interfaces, making it harder for attackers to exploit side-channel vulnerabilities. You can also implement advanced intrusion detection tools without worrying about impacting other tenants’ performance.
Scalability and Support
Some assume dedicated hosting lacks scalability. But providers like us at Melbicom have simplified server provisioning—our inventory includes more than 1,000 ready-to-go server configurations that can be deployed quickly, often in hours. Monitoring and support are likewise robust. We at Melbicom monitor for unusual traffic patterns, offering DDoS protection where needed. Free 24/7 technical support ensures you can resolve issues anytime. That kind of tailored assistance can be indispensable for mission-critical workloads.
Key Industry Trends Driving Dedicated Server Hosting
Analysts link the rise of dedicated hosting to two major drivers: low-latency requirements and relentless cyber threats. As next-gen networks and real-time applications proliferate, more businesses need near-instant responses. A recent market survey indicated an annual growth rate of over 20% for low-latency communications, suggesting continued demand for infrastructure that can meet sub-10 ms round-trip times.
On the security front, multi-tenant attacks—especially cross-tenant exploits—have grown more sophisticated. This trend pushes organizations toward single-tenant architectures. In some cases, a hybrid model is adopted: critical workloads run on dedicated machines, while less sensitive tasks reside in elastic cloud environments. The net effect is a growing share of infrastructure budgets allocated to hosting on a dedicated server.
| Trend | Impact on Dedicated Hosting |
|---|---|
| Rise of Ultra-Low Latency Apps | Boosts demand for physically close servers offering sub-10 ms or microsecond-level performance |
| Escalating Cyber Threats | Single-tenant designs isolate vulnerabilities; advanced security controls become essential |
| Cost Predictability | Fixed-rate dedicated servers can be more economical at scale than variable cloud pricing |
Conclusion: Single-Tenant Infrastructure for Speed and Safety
For mission-critical services seeking sub-10 ms response times and robust security, single-tenant dedicated infrastructure remains the gold standard. Multi-tenant environments have improved, but noise issues and cross-tenant risks persist. By taking full advantage of custom firewalls, private networking, and hardware root-of-trust, you create a fortified environment with consistent low latency.
Get Your Dedicated Server
Deploy a high-performance dedicated server in hours and gain ultra-low latency with robust security.
We are always on duty and ready to assist!
Blog
Why Choose a Netherlands Dedicated Server for EU Reach
If you possess a digital company that requires seamless access throughout Europe, you need a top-class internet hosting site. You find that in the Netherlands. With high-bandwidth connectivity and a commitment to greener energy solutions, the cost‑effective infrastructure in the Netherlands beats that of most other countries. On top of that, the Netherlands has very solid data protection laws, which adds another layer of “trust and security” coating to this pivotal internet hosting location. Until recently, many businesses stuck with data centers located in their home countries. Those days are over. Almost any Dutch data center is faster, more reliable, and more in line with the kinds of legal requirements businesses are now compelled to meet.
The low‑latency pan‑European connectivity provided by a Netherlands dedicated server is a huge advantage to any digital enterprise looking to operate across the EU. To understand why, let’s take a look at the benefits and how the country’s privacy law alignment and sustainability focus benefits can help with growth and success.
AMS‑IX: Providing Pan‑European Low Latency Exchanges
Low latency is vital to exchange speeds, and the latency rests upon traffic routes. Amsterdam is situated at the core of Europe’s network map, and hosts one of the world’s largest peering hubs, the Amsterdam Internet Exchange (AMS‑IX). AMS‑IX interconnects with over 1,200 networks and handles traffic peaks (over 14 Tbps) on a regular basis. Among its peers are Tier‑1 carriers and global content providers, which shortens cross‑continental data routes, lowering latency dramatically.
The round‑trip times coming out of Amsterdam are impressive. Latency tests sent to Frankfurt and Paris and back take roughly 10–15 ms 1.2. and back in under 20 ms. Southern Europe, such as Madrid, shows a response of 30–40 ms. The table below demonstrates the results of some typical round‑trip delays:
| Test Destination | Round‑Trip Latency Approximation |
|---|---|
| London, UK | ~15 ms |
| Frankfurt, DE | ~10 ms |
| Paris, FR | ~16 ms |
Table. Latency information gathered from Epsilon Global Network.
Businesses that operate with a nearby server presence stand to reap the benefits. Despite being a single point of presence in Amsterdam, the packet delivery speed through an AMS‑IX connection can work to an enterprise’s advantage. Amsterdam is already a major juncture for Web traffic, with a peering layer that enables the breakdown of overall traffic to local destinations. For an enterprise using an AMS‑IX connection in Amsterdam, the connection is faster than a point‑to‑point Web service in the same city. The Web services, SaaS, e‑commerce, and streaming businesses that do use the connection seem pleased with the results.
At Melbicom, our outbound and inbound traffic passes through high‑capacity, multi‑redundant fiber networks that take advantage of the direct peering at AMS‑IX and other low‑latency exchanges. Such stability prevents any bottlenecks, ensuring that our connections remain up and accessible all the time, hitting us with reliable speeds that cater to any heavy workloads that demand dependability.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Assurance
The Netherlands has a strong commitment to data privacy, meaning its hosting must conform to many worldwide data protection laws. Given the country’s EU status, it adheres to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) but is also regulated by local rules and oversight. The standards are much higher for providers operating within the jurisdiction of the Netherlands when it comes to data handling, breach notifications, and user privacy, which ensures trust for the end users.
With such strong regulation in Dutch laws, enterprises hosted within have better legal clarity and consistency across European markets. Typically, when operating in various locations, enterprises are faced with differing national regulations to comply with. The Netherlands’ robust implementation of EU directives gives a strong framework that ensures compliance. This is especially advantageous for those collecting or processing sensitive information, and fosters reassurance for customers who can relax knowing their personal or corporate data is stored and processed securely.
Local hosting was once favored for meeting individual data mandates, but with the Netherlands’ GDPR integration and data security priorities, there has been a real shift in perspective. Today, the merits of the advanced data‑centered ecosystems hosted in Amsterdam are being recognized by businesses. They understand increasingly that the impressive performance, coupled with its comprehensive legal protection, makes it unbeatable. At Melbicom, this protection is further reinforced through strict security controls, ISO/IEC 27001 certifications, and around‑the‑clock monitoring. Our Amsterdam data centers ensure secure, compliant workloads regardless of scale.
Sustainably Powered Data Centers
Sustainability is a subject of heated current‑day discourse, and many businesses are attempting to embrace it in order to minimize their environmental footprints. A good number of the data centers situated in the Netherlands use renewable energy sources, as the country has made a commitment to much greener energy solutions. The Dutch Data Center Association states that around 86% of the data centers in the Netherlands use wind, solar, or hydro energy, and this figure is set to increase in the coming years.
Operators are also taking on more and more 100% renewable energy contracts, innovating their practices with advanced cooling systems and recycling waste heat to increase efficiency and reduce consumption. The country’s Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) ratios hover around at the 1.2 mark, where competitors show PUE levels above 1.5.
Enterprises can significantly lower their carbon footprint per compute cycle by tapping into the infrastructure of a dedicated server hosting arrangement. This helps businesses meet sustainability benchmarks and benefits the environment, which in the modern world is important to users with eco‑conscious mindsets. Melbicom’s facility, based in Amsterdam, benefits from the nation’s green initiatives, and our Tier III and Tier IV data center servers prioritize energy efficiency, lowering your environmental impact and promoting sustainability without sacrificing performance.
1 Gbps Unmetered Dedicated Servers for Cost‑Efficient Bandwidth
Cost efficiency is another major factor that makes dedicated Netherlands servers so attractive. As Amsterdam is such a prime interconnection hub with high‑capacity bandwidth, it can afford to price itself very competitively among carriers. This higher transit capability equates to generous unmetered or high‑limit data plans.
Often, a dedicated server Netherlands option offers 1 Gbps unmetered plan, which would be far more expensive in some other locations in Europe. With unmetered hosting, large volumes of traffic can be handled without being charged per gigabyte, which is a big advantage. For clients with demanding throughput, Melbicom can provide multi‑gigabit uplinks cost‑efficiently by leveraging the rich peering offered by the Netherlands connections, regardless of how bandwidth‑hungry the applications may be. Whether it is streaming media, content delivery, or IoT platforms, operations run smoothly without the fees snowballing.
Smaller markets operating from local data centers are unable to match the low‑latency routes and economical high‑bandwidth packages that the Netherlands boasts with its mature market. They are also more accessible; you don’t need to be a tech giant to benefit. 5 Gbps or 10 Gbps server configurations are readily available for mid‑sized enterprises and can be scaled. Companies expecting growth that need to maintain continuity and deliver high‑quality experiences will find a dedicated server Netherlands arrangement ideal for coping with any fast‑growing traffic demands across Europe.
Shifting the Historical Local‑Only Mindset
In the last decade, the shift from local‑only hosting to centralized Dutch infrastructure has been accelerating. Historically, servers were fragmented and kept within their respective national borders due to barriers surrounding performance and legalities. These days, those barriers are largely non‑existent, and cross‑border links are faster than ever before.
With the introduction of high‑speed fiber routes that span entire continents, the connections between Amsterdam and all major European cities are low‑latency and consistent. Add to that the unified data protections that come under GDPR mandates, and you have a secure solution for storage and handling in every EU state. These factors combined are the force that has driven markets toward dedicated servers in the Netherlands in recent years, making it a hub for pan‑European activities.
Even many smaller markets now route their internet traffic via Amsterdam, creating a redundant “trombone routing” effect that wastes time and resources. Opting to physically host from the Netherlands simplifies infrastructure and boosts performance and speed. We have seen a rise in clients consolidating their needs at Melbicom, making the leap to a single or clustered environment in our Amsterdam data center. This shift comes with cost benefits and provides predictable uptime.
Conclusion: Achieve Pan‑European Reach Through the Netherlands
Amsterdam sits at the heart of operations in the role of Europe’s internet capital. AMS‑IX’s peering reigns superior, and the country’s dedication to sustainability means power‑efficient data centers. The nation’s digital operations are ruled by strong regulatory agreements, which give it further advantages to businesses and enterprises. For low‑latency responses that cover the whole of Europe, a dedicated server Netherlands strategy gives you the speed and power required without having to complicate your hosting solution with multiple local deployments. Choosing to host in Amsterdam provides a unification between secure high‑speed bandwidth needed for demanding workloads and compliance, while allowing you to tap into the nation’s green power efforts.
Order a Netherlands Dedicated Server
Deploy high‑performance, low‑latency servers in Amsterdam today and reach users across Europe with ease.
We are always on duty and ready to assist!
Blog
Singapore’s Sustainable Data Center Expansion
Singapore serves as a fundamental data center center with more than 70 facilities combined with 1.4 GW of operational capacity. A temporary data center construction ban implemented by the government caused a brief halt in growth because of power supply and sustainability worries. The “capacity moratorium” did not affect Singapore’s standing as a data center location. The country maintained its position as a leading data center location in the world during that brief period even though new development was paused.
After the construction pause, Singapore resumed data center development through programs that enforced strict environmental standards. The goal focuses on maximizing power efficiency alongside promoting renewable energy usage while lowering carbon emissions. The 80 MW pilot allocation received immediate approval from authorities before plans emerged to create sustainable data center capacity reaching 300 MW. The Data Centre Green Policy of Singapore requires sophisticated cooling systems with waste heat recovery capabilities and state‑of‑the‑art infrastructure to achieve PUE levels below 1.2. The implementation of this method results in the best dedicated server in Singapore becoming part of a world‑class data center with Tier III or Tier IV standards which achieve maximum environmental efficiency.
The Expansion of Subsea Connectivity
Singapore stands as a strategic global location because it connects major submarine cable routes which span between Asia‑Pacific, Europe and North America. The country has maintained its role as a telecommunications gateway for the region through its strategic position. The total number of submarine cables operating in Singapore reached 26 systems during 2023. The upcoming submarine cable installations by Google and Meta together with other companies will bring the total count to more than 40 systems.
The Bifrost and Echo systems along with other major cable projects establish direct US West Coast connectivity for Singapore. Projects such as Asia Direct Cable and SJC2 enhance the connectivity between East and Southeast Asian regions. The purpose of these cables minimizes latency across both trans‑Pacific and intra‑Asian routes which maintains Singapore’s status as a region with minimal round‑trip times.
The international bandwidth of Singapore supports hosting providers to deliver extremely fast uplink speeds to their customers. For instance, the server support of 200 Gbps at Melbicom enables us to serve large streaming or transaction‑intensive platforms. Physical diversity of cables creates robust route redundancy for the region. Traffic rerouting through alternative systems becomes possible when one cable experiences downtime. The result of these upgrades benefits enterprise customers by providing constant network performance and high availability for their Singapore dedicated servers.
The substantial infrastructure investments demonstrate Singapore’s determination to establish itself as the supreme connectivity center for Asia‑Pacific. The government predicts digital economy investments from submarine cable projects and data center expansions to reach above US$15 billion. The infrastructure upgrades create essential connectivity support for businesses which choose to deploy their operations in the region.
Cybersecurity and Regulatory Strength
Singapore maintains superior physical infrastructure together with one of the most powerful cybersecurity frameworks worldwide. The Global Cybersecurity Index places Singapore among the world leaders because of its outstanding performance in cyber incident response and threat monitoring and legal standards. The Cyber Security Agency of Singapore (CSA) maintains fundamental security protocols while establishing quick response systems to protect data centers and other critical infrastructure.
A data center‑friendly regulatory framework exists as the second essential factor which supports the industry. The authorities maintain specific data handling regulations through the Personal Data Protection Act (PDPA) as well as guidelines for electronic transactions and trust services. The combination of strong privacy measures with an adaptable regulatory environment has attracted numerous fintech, crypto and Web3 startups to the market. Singapore stands apart from countries with ambiguous laws through its clear position which creates stability.
Enterprises find comfort in dedicated server hosting within Singapore because the government maintains stable legal frameworks and makes significant digital asset protection investments. The power grids operate with stability and disaster recovery planning reaches complete levels while network protection reaches advanced stages. The combination of these elements lowers the probability of downtime and compliance breaches which is why financial institutions and compliance‑heavy organizations select Singapore for their dedicated servers.
Latency Comparison: Singapore vs. Other Asian Hubs
Latency stands as an essential factor which determines user experience quality because it affects real‑time services such as gaming and video streaming along with financial operations. The combination of geographical location with numerous submarine cables enables Singapore to provide significantly lower round‑trip times to Southeast Asia and Indian destinations than its neighboring markets.
The following simplified table shows estimated latency times (in milliseconds) that measure the distance between Singapore and Mumbai and several major destinations.
| Destination | From Singapore | From Mumbai |
|---|---|---|
| Jakarta | ~12 ms | ~69 ms |
| Hong Kong | ~31 ms | ~91 ms |
Table: Approx. round‑trip latency from data centers in Singapore vs. India.
The differences between these latency values are essential for online gaming (which requires sub‑50 ms pings) as well as high‑frequency trading and HD video conferencing. The direct network connections of Singapore to Europe and North America decrease the requirement for multiple network transmission points.
A dedicated server solution in Singapore leads to significant performance improvements in application response times for organizations that target regional user bases. The excellent presence of top‑tier ISPs and content providers and Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) in Singapore accelerates traffic handoffs which results in superior user experiences.
Driving Demand: iGaming, Web3, and Crypto
Singapore data centers serve multiple industries yet several fast‑growing fields stand out among them. Online betting companies and online casinos serving Southeast Asian audiences need dependable and robust infrastructure to operate their betting platforms. The platforms achieve excellent redundancy and strong data protection rules as well as fast network performance to regional players because of Singapore.
Singapore has become a destination for Web3 and crypto firms to expand their operations. The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) has established digital payment and blockchain company regulations which positions the nation as an ideal location for crypto exchanges, NFT marketplaces and DeFi projects. The platforms execute complex transactions at high volumes which requires powerful servers to process them effectively. The data centers in Singapore deliver specialized hardware configurations with GPU‑based systems which support compute‑intensive tasks while maintaining low latency for both local and global transactions.
Enterprise SaaS together with streaming services and e‑commerce operate their central hosting infrastructure from Singapore. The fundamental reason organizations select Singapore remains stable because of its combination of low‑latency connectivity, regulatory certainty, robust security and proven resilience.
Conclusion: Singapore’s Edge in Dedicated Server Hosting
Singapore maintains its position as the top data center location in the Asia‑Pacific region because it balances its development strategies. After implementing sustainability requirements on data center approvals, the country regained its position as a leading dedicated server hosting location through new green data centers and extensive subsea cable networks and high cybersecurity ratings. Organizations across Asia are increasingly dependent on powerful infrastructure with low latency which Singapore successfully provides to its clients.
Order a Server in Singapore
Deploy a high‑performance dedicated server in our Tier III Singapore facility and reach Asia‑Pacific users with ultra‑low latency.
We are always on duty and ready to assist!
Blog
Choosing the Right Web Application Hosting Strategy
Modern web deployments demand strategic infrastructure choices. The growth of web traffic and rising user demands have led to numerous web application hosting options: dedicated servers in global data centers, multi‑cloud structures, edge computing, and hybrid clusters. The decision to select a correct approach depends on workload characteristics as well as elasticity requirements, compliance rules, and geographic latency limitations. The article provides a useful selection framework to evaluate the appropriate hosting model.
Decision Matrix Criteria
Workload Profile
Stateful vs. stateless: Stateless services (e.g., microservices) maintain easy horizontal server scalability because they do not store state information. The handling of memory and session data becomes crucial when implementing stateful applications which include Java sessions and real‑time data services.
CPU, memory, or I/O bound: A media streaming platform with huge I/O needs might prioritize high‑bandwidth servers. An analytics tool that depends on raw computational power will require different server specifications than streaming platforms which need high bandwidth servers. A dedicated server with predictable resources delivers superior performance than multi‑tenant virtualization for Java web applications under heavy concurrency conditions.
Elasticity
Predictable vs. spiky demand: Dedicated servers excel when loads are consistent, as you can plan capacity. Cloud or container environments enable auto‑scaling to prevent bottlenecks during sudden traffic surges (e.g., product launches). A common strategy involves keeping dedicated servers operational for base capacity while activating cloud resources during times of peak demand.
Compliance and Security
Organizations must use either single‑tenant or verified data center hosting to process regulated information. Security configurations and physical access become more manageable through dedicated servers which provide complete control to users. Public clouds offer compliance certifications (HIPAA, PCI‑DSS, etc.), yet multi‑tenant environments need users to place their trust in provider‑level isolation. Enterprises usually maintain regulated data within single‑tenant or private hosting environments.
Geographic Latency
Physical distance influences response times. Each 1,000 km adds roughly 10 ms of latency. Amazon discovered that a 100 ms rise in response time results in a 1 % decline of sales revenue. Server placement near user clusters stands essential for achieving high performance. Some organizations use edge computing along with content delivery networks (CDNs) to distribute content near user locations. Melbicom operates 20 global data centers, plus a CDN spanning 50+ cities for low‑latency access.
Comparing Hosting Approaches
| Paradigm | Strengths | Trade‑offs |
|---|---|---|
| Dedicated Servers | Single‑tenant control, consistent performance, potentially cost‑efficient at scale. Melbicom provides customers the ability to deploy servers in Tier III or IV data centers that offer up to 200 Gbps bandwidth through server rental options. | Manual capacity planning, slower to scale than auto‑provisioned cloud. Requires sysadmin expertise. |
| Multi‑Cloud | Redundancy across providers, avoids lock‑in, can cherry‑pick specialized services. | Complexity in management, varying APIs, potential high data egress fees, multiple skill sets needed. |
| Edge Computing | Reduces latency by localizing compute and caching. Real‑time applications as well as IoT devices and content benefit most from this approach. | Complex orchestration across multiple mini‑nodes, data consistency challenges, limited resources at each edge. |
Dedicated Servers
Each server operates independently on dedicated hardware which eliminates the performance problems caused by neighboring applications. CPU‑ and memory‑intensive applications find strong appeal in the unadulterated computing capabilities of dedicated servers. Through our dedicated server deployment at Melbicom, you can acquire servers in hours and enjoy bandwidth options reaching up to 200 Gbps per server. The machine costs remain constant through a fixed monthly or annual payment which covers all usage. The reliability of Tier III/IV facilities matches uptime targets from 99.982–99.995 %.
The advantages of dedicated infrastructure come with the requirement for more direct hands‑on administration. The process of scaling up requires physical machine additions or upgrades instead of cloud instance creation. Workloads such as large databases and specialized Java web application stacks benefit from this feature because they require precise OS‑level tuning.
Multi‑Cloud
The use of multiple cloud providers decreases your dependence on any single cloud platform. The major advantage of redundancy is that it is extremely unlikely to see simultaneous outages of all providers. Surveys reveal that 89 % of enterprises have adopted multi‑cloud computing, but the complexity level is high. Juggling different APIs makes it harder to handle monitoring, networking, and cost optimization tasks. The costs of moving data outside of clouds can become quite expensive. A unifying tool such as Kubernetes or Terraform helps maintain consistent deployments.
Edge Computing
The processing of requests by edge nodes located near users leads to minimized latency. A typical example is a CDN that caches static assets. The deployment of serverless functions and container instances on distributed endpoints within advanced edge platforms enables real‑time service operations. Real‑time systems together with IoT analytics and location‑based apps require local processing because they need responses within 50 milliseconds. The distribution of micro‑nodes across various geographic locations creates challenges when trying to synchronize them. The network must redirect traffic to other edge nodes when a city‑level outage occurs.
Hybrid Models
Hybrid cloud integrates on‑premises (or dedicated servers) with public cloud. The deployment of sensitive data on dedicated servers combines with web front‑ends running on cloud instances. Kubernetes functions as a container orchestration platform to provide infrastructure independence which enables the deployment of identical container images across any environment. This method unites the cost efficiency of dedicated infrastructure with the scalability benefits of the cloud. The main difficulty lies in managing the complexity because synchronizing networks with security policies and monitoring across multiple infrastructures becomes extremely challenging.
Why Hybrid? Every team identifies that a single environment does not fulfill all their requirements. A cost‑conscious organization requires steady monthly fees for core capacity needs but also wants cloud flexibility for peak situations. Containerization helps unify it all. Each microservice becomes deployable on dedicated servers and public cloud infrastructure without significant difficulties through containerization. Robust DevOps practices together with observability represent the essential components for success.
Mapping Requirements to Infrastructure
The combination of strategic environments usually leads to the best results. Evaluate the requirements of statefulness and compliance as well as latency and growth patterns when deciding.
- Stateful and performance‑sensitive apps require dedicated servers for direct hardware access to thrive.
- The use of auto‑scaling and container platforms in the cloud works best for unpredictable workload needs.
- The placement of compliance‑driven data requires single‑tenant or private systems within specific regions.
- Deploying in data centers near users combined with a CDN or edge computing provides the best results for latency‑critical applications.
Each piece in your architecture needs to match the requirements of your application to achieve resilience and high performance. The combination of dedicated servers in one region with cloud instances in another and edge nodes for caching allows you to achieve low latency, strong compliance, and cost optimization.
Melbicom’s Advantage
The Tier III and IV data centers of Melbicom offer dedicated servers with 200 Gbps bandwidth per server to support applications requiring constant high throughput. Your solution will become more effective when you integrate dedicated servers with cloud container orchestration and a global CDN for latency reduction. The adaptable infrastructure provided by Melbicom enables you to develop a solution that addresses the specific requirements of your application.
Launch Dedicated Servers Fast
Deploy high‑bandwidth dedicated servers in 20 modern data centers worldwide and scale confidently.
We are always on duty and ready to assist!
Blog
How to use Kubernetes with vMesh
This guide details the process of deploying Kubernetes (K8s) clusters on vMesh private networks, providing low latencies, improved security and network isolation for your containerized applications.
Prerequisites
- Multiple Linux VPS Cloud instances with at least Ubuntu 22.04 installed
- Administrative (root) access to each VPS
- vMesh Private network connectivity between VPS instances. You may refer to this guide.
We will replicate the following network topology as an illustrative example:
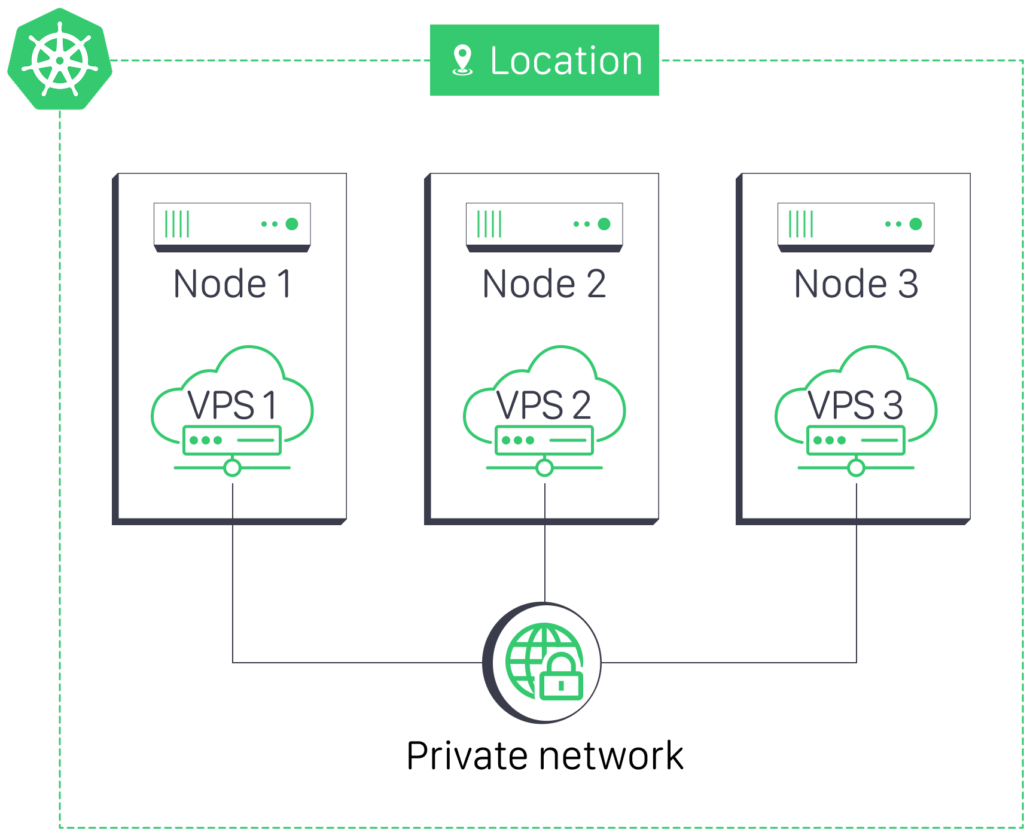
Network Configuration
Configure Private Network Interfaces
Edit the /etc/network/interfaces file on each VPS:
VPS Cloud 1:
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet static
address 10.10.0.2
netmask 255.255.255.0
VPS Cloud 2:
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet static
address 10.10.0.3
netmask 255.255.255.0
VPS Cloud 3:
auto eth1
iface eth1 inet static
address 10.10.0.4
netmask 255.255.255.0
Apply Network Configuration
Restart the networking service on each node:
sudo systemctl restart networking.service
Verify Connectivity
Test connectivity between all nodes:
ping 10.10.0.3
ping 10.10.0.4
Kubernetes Installation
Install Required Packages
Update package lists and install prerequisites:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
Add Kubernetes apt repository:
curl -s https://packages.cloud.google.com/apt/doc/apt-key.gpg | sudo apt-key add -
echo "deb https://apt.kubernetes.io/ kubernetes-xenial main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/kubernetes.list
Update package lists again and install Kubernetes components:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y kubelet kubeadm kubectl
sudo apt-mark hold kubelet kubeadm kubectl
Configure Container Runtime
Install and configure containerd:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y containerd
Create default configuration:
sudo mkdir -p /etc/containerd
containerd config default | sudo tee /etc/containerd/config.toml
Update configuration to use systemd cgroup driver:
sudo sed -i 's/SystemdCgroup = false/SystemdCgroup = true/g' /etc/containerd/config.toml
Restart containerd:
sudo systemctl restart containerd
sudo systemctl enable containerd
Initialize Kubernetes Cluster
On the control plane node (VPS Cloud 1):
sudo swapoff -a
sudo sed -i '/ swap / s/^\(.*\)$/#\1/g' /etc/fstab
Initialize the cluster with private network CIDR:
sudo kubeadm init --pod-network-cidr=10.10.0.0/24 --apiserver-advertise-address=10.10.0.2
Set up kubectl for the current user:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube
sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
Install and Configure Calico CNI
Download and apply the Calico manifest:
curl https://docs.projectcalico.org/manifests/calico.yaml -O
kubectl apply -f calico.yaml
Configure Calico to use the private network CIDR:
kubectl set env daemonset/calico-node -n kube-system IP_AUTODETECTION_METHOD=cidr=10.10.0.0/24
Troubleshooting
Network Issues
- Verify interface configuration with
ip addr show - Check routing tables with
ip route - Test connectivity with
pingandtraceroute
Kubernetes Issues
- Check pod status:
kubectl get pods -A - View logs:
kubectl logs <pod-name> -n <namespace> - Check node status:
kubectl describe node <node-name>
We are always on duty and ready to assist!
Blog

How vMesh Enhances VPS Private Networks
Businesses all over the world face the dual challenge of managing massive data flows while ensuring robust security and system reliability. It is for this reason that virtual private servers have become a cornerstone of modern IT strategies. That’s because they offer the flexibility of cloud hosting along with the robustness of dedicated resources.
However, the full potential of VPS is only unlocked through sophisticated network solutions that optimize performance and security. That’s where vMesh enters the scene as a transformative solution.
What is vMesh?
vMesh is a networking solution that connects different VPSes within a secure and private network. Essentially, it acts like a private highway for data.
It moves speedily and safely between servers minus the risks and delays that can occur when data travels over the public internet. Because vMesh improves security and performance, it’s usually adopted by businesses that handle sensitive information or those that require fast, reliable communication between their servers.
Understanding VPS Private Networks
In order to understand what vMesh is and why anyone would even need it in the first place, let’s first divert our attention to a VPS private network. This is an isolated network environment specifically designed for VPS instances within a data center.
For starters, a VPS instance is basically a virtual server that you can use as if it were your own dedicated server. But what makes it unique is that it runs on a larger, more powerful server along with other VPS instances. As a result, it comes with private resources like CPU, memory, and storage on a shared physical server.
What’s more, you’re fully in control of your server environment. For instance, among other things, you get to decide the operating system and the applications you install.
Another benefit is that getting a VPS instance is cheaper than renting an entire physical server. To give you some perspective, you can use it to host websites, applications, and databases that require more control and resources, something many shared hosting environments don’t offer.
Benefits of VPS Private Networks
Now let’s dig a little bit deeper into the benefits of VPS private networks.
Enhanced Security
This setup limits network access to authorized users and devices only. Consequently, it protects sensitive data from external threats and breaches, such as hacking, theft, and malware injections.
Improved Performance
With VPS private networks, you won’t need to worry about the overcrowding that the public internet is known for. Bear in mind that overcrowding usually happens when numerous data streams compete for bandwidth.
What makes this private network different is that it creates a dedicated, isolated pathway for data between servers. This setup prevents data from being delayed or disrupted by other traffic.
Now you understand why VPS private networks have quicker data transfer rates and more consistent communication between servers. This results in faster, more reliable performance for applications and services running on the VPS.
Scalable Infrastructure
VPS private networks enable businesses to scale their network resources efficiently. Such businesses can quickly adapt to changing demands without significant downtime or reconfiguration.
How vMesh Functions Within VPS with Private Networks
vMesh integrates with existing VPS infrastructures. Usually, this integration creates a high-speed, low-latency private network within a single data center (IntraDC).
The network fabric we’ve described above acts like a dedicated expressway for data packets. That’s because it allows data to travel securely and efficiently without relying on the public internet route, which, in most cases, is prone to congestion.
Here is a common real-world use case of vMesh for building a scalable, high-traffic, secure and highly available VPS architecture
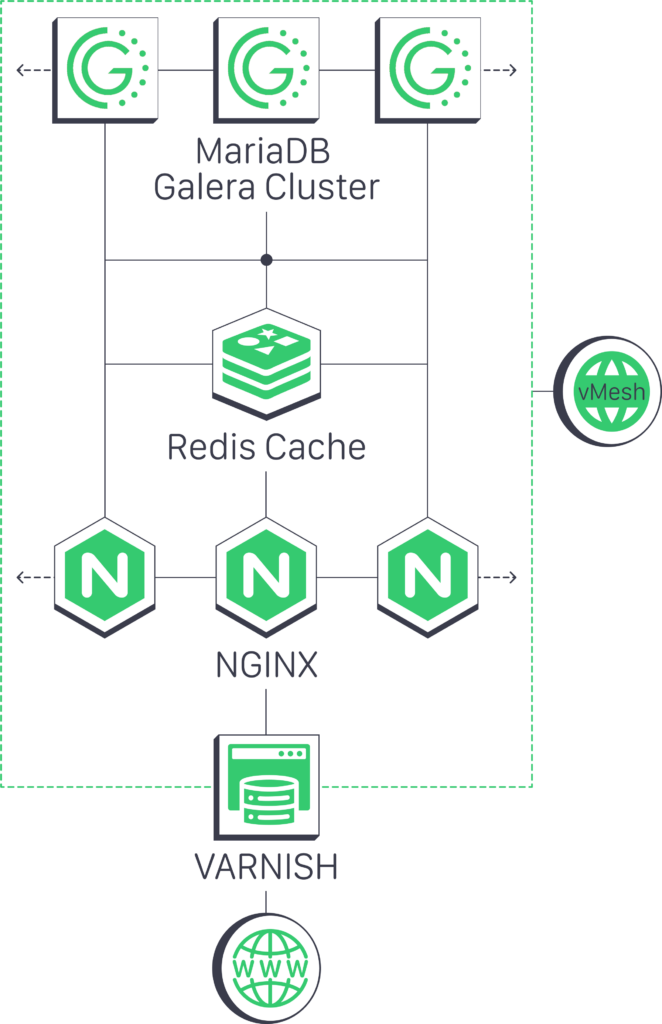
How vMesh Benefits High-Traffic Sites and Microservices
vMesh is a powerful networking solution for bridging the gap between private networks and Virtual Private Cloud environments. Here’s how high-traffic sites and microservices stand to benefit from this networking solution.
Optimized for Microservices
vMesh provides a dedicated private network for connecting VPS instances. They solve the problem of congestion and security risks that’s usually common with public networks by providing low-latency, high-speed connections between components. This makes it a great choice for systems like MySQL Galera replication, where fast and reliable communication is critical.
Scalability and High Bandwidth
With vMesh, businesses can scale effortlessly. Its ability to cumulate port speeds—supporting up to 10 Gbps bandwidth—combined with an unlimited private IP pool, ensures flexibility and growth without compromising performance.
Redundancy and Reliability
While redundancy is not its primary focus, vMesh’s design ensures dependable connections. It achieves this by minimizing downtime and enhancing data availability. By leveraging secure private interfaces, vMesh helps businesses avoid congestion while maintaining a strong and powerful network infrastructure.
Real-Life Use Cases of vMesh
To help you better understand the whole point of using vMesh, let’s look at real-life examples of scenarios where this system can save the day.
eCommerce Platforms
Think of Black Friday as an example. No doubt that this is one of the biggest shopping days in the United States and many locations across the world.
As an eCommerce business owner, you want your store ready for this day. There’s literally zero room for errors, especially on this special day.
And if you doubt that, the story of Lowe’s website crash on Black Friday in 2018 should tell you everything you need to know about the importance of having a fully redundant and scalable infrastructure.
By employing Melbicom’s vMesh, eCommerce companies can efficiently manage sudden surges in traffic. That’s because this system has robust load balancing and automatic failover capabilities.
Gaming Platforms
For online gaming platforms, any form of delay is the enemy of player satisfaction. Regardless of how much they love that particular game, no player wants to sit around waiting for a server that takes too long to load.
That’s why vMesh ensures ultra-low latency and high throughput with data centers across 17 different locations around the globe. The 1Gbit/s low-latency Layer 2 intra-DC connection, in particular, helps facilitate real-time interactions in multiplayer environments.
Healthcare Data Management
With vMesh, healthcare providers can exchange medical records quickly and safely across facilities. This is one way of ensuring compliance with stringent regulations like HIPAA in the U.S., for example.
Also, using vMesh in healthcare data management can improve the quality of patient care. When healthcare providers have access to comprehensive, up-to-date medical records, they are able to make better-informed decisions, offer timely medical interventions, and provide personalized care plans.
Financial Services
In matters of finance, data privacy is paramount. Sensitive financial transactions, just like healthcare data exchanges, require secure, private connections to protect critical information. vMesh from Melbicom provides an advanced networking solution that safeguards financial data against breaches, meeting even the strictest security and compliance standards.
Beyond privacy, vMesh also supports real-time data transfers essential for financial transactions. In stock trading, for instance, a fraction of a second could be the difference between making profits or losses.. That’s where vMesh’s low-latency design kicks in for seamless trading.
With vMesh, financial organizations can remain operational, protect sensitive data, and confidently meet industry regulations, just as healthcare providers do when securing patient information.
VPN vs. VPS Private Network
Both VPNs and VPS private networks enhance security by isolating data from the public internet. However, they differ in operation and benefits. Here’s how.
VPNs secure data across public networks through encryption. This extra layer of security is meant to protect sensitive information as it travels over untrusted environments.
No doubt that’s an effective way of protecting sensitive data, but the biggest issue here is that the encryption can increase CPU usage. This is especially common when handling heavy workloads.
VPS private networks, on the other hand, don’t experience CPU strain. That’s because they operate within a trusted, localized infrastructure.
Additionally, VPS private networks often include dual network ports. One port handles private communication and the other for public access. This design ensures secure and efficient data flow within the network.
Interestingly, although they all provide unique benefits, these technologies can still work together. Take, for example, organizations needing top-level security.
By combining a VPN with a VPS private network, businesses can extend their private infrastructure to offsite locations. This setup is particularly useful for secure backups or connecting remote systems to the company network.
Future Trends in VPS Networks
VPS networks have important roles to play now and in the future. For perspective, let’s look at two scenarios: IoT integration and AI and machine:
IoT Integration
IoT devices usually generate a vast amount of data that needs to be processed and analyzed in real-time. In such a case, VPS networks can help these devices handle the high volume and velocity of data traffic.
AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning applications require a lot of computational power and data storage. That’s because they usually process large datasets to train models that can perform tasks like predictive analytics, natural language processing, or even image recognition.
We’ll likely see a future where VPS networks supporting these applications will become highly scalable and flexible. That way, they’ll be able to accommodate the variable workloads and storage needs associated with AI and machine learning tasks.
Why vMesh Is Future-Proof
Fortunately for its users, vMesh is a technology that works in the present with its eyes set on the future. Here’s why and how:
Efficient Data Flows
vMesh optimizes the route data takes through the network. This strategy helps reduce latency and also ensures that data packets are delivered quickly and reliably. This is particularly important for IoT and AI applications where timely data processing matters.
Enhanced Security Protocols
We’ve seen that IoT devices are now beginning to handle AI-generated data. This trend is expected to grow even faster in the near future. That’s where the importance of network security comes in.
vMesh enhances security measures to protect data from emerging threats. This includes threats introduced by the broad and often less secure surface area of IoT devices and the valuable intellectual property contained in AI data.
Future-proofing
vMesh is adaptable. In other words, it can work with new technologies as they develop. This adaptability ensures that VPS networks can continue to support new applications and technologies. And the best part is that there’ll be no need to overhaul the existing network infrastructure.
Environmental and Cost Impact of Melbicom’s vMesh
Implementing vMesh in data centers isn’t only about boosting network performance and security. Rather, it’s also one of the many things you can do to save the environment and manage costs. Here’s how.
Energy Efficiency
One of the most compelling benefits of vMesh is its ability to enhance energy efficiency across network systems. As data demands grow, traditional data centers may find it challenging to manage increased energy consumption. This mostly happens because of the need to power and cool physical servers.
vMesh addresses this issue by optimizing data flow efficiency, which reduces the workload on individual servers. When that happens, it decreases the amount of energy required to keep these servers up and running.
In addition, vMesh’s data routing capabilities mean that less processing power is wasted. On top of that, servers can operate at lower temperatures. This reduction in heat generation reduces the need for constant cooling.
It’s also worth noting that cooling is a major expenditure when you’re dealing with data centers. However, since this system keeps servers active only when necessary, these data centers are able to operate more sustainably.
Cost Effective Operations
Granted, managing such a setup costs money. However, adopting vMesh makes a huge difference in expenditures.
First, since it reduces the physical infrastructure needs through better utilization of existing servers, companies can cut down on capital expenditures typically spent on additional hardware. Fewer servers and network devices mean lower initial setup costs and reduced ongoing expenses for maintenance and upgrades.
Secondly, the automation features of vMesh, such as load balancing and automatic failover, minimize the need for manual IT interventions. That further reduces operational costs. The combined savings on energy, hardware, and labor also contribute to a leaner, greener operational model.
Finally, you’ll end up with a win-win situation. That’s because the cost-effectiveness also trickles down to the consumer. Our order page, for example, is a true testimony of just how we can provide top-notch server solutions using vMesh without overcharging our clients.
Let Melbicom’s vMesh Transform Your Network
The bottom line here is that vMesh is revolutionizing how businesses approach their network infrastructure. This is especially important given that we’re now living in a digitally dominated-world.
By integrating vMesh into their VPS environments, companies can achieve unprecedented levels of scalability, security, and performance.
Is your business prepared to enhance its network capabilities with vMesh? Visit our order page and choose your vMesh package to get started. It only takes a few minutes!
We are always on duty and ready to assist!
Blog

What is SSL and how to choose one for your website
If you look at the address bar in the browser tab, you can see the symbols http or https before the name of any website. This refers to the protocol used to connect a user’s browser to the website. HTTP stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol. It’s great for transferring messages, but unfortunately it doesn’t provide enough protection for your Internet connection.
The HTTPS protocol is used to protect data. The letter “S” here means “security” and implies the use of a cryptographic encryption. HTTPS requires a website to have a special SSL certificate. This is a unique digital signature that confirms authenticity and security. Packets over https are transmitted in encrypted form, and even if a hacker intercepts them, he will not be able to decrypt and use them.
It is possible to check if a website has an SSL certificate by checking the lock icon next to its address. If it is missing, the browser will display a warning about insecurity: the packets you send may be stolen It is strictly forbidden to create a personal profile on such a resource and especially to enter bank card credentials.
Who needs an SSL certificate?
SSL certificate is essential for web resources that involve working with personal data. It is impossible to secure transactions on marketplaces and other services without an encrypted connection. Cryptography reduces the vulnerability and probability of data interception by intruders. In addition, there are other tangible benefits:
- Increased trust of visitors. People get used to see the lock icon in the address bar. All the large IT-projects switched to HTTPS a long time ago. SSL certificate shows a visitor that he is protected.
- Ability to connect third-party services. Modern payment and auxiliary web services (e.g., various Google tools) can only work with IT resources that have an SSL certificate. If you need to integrate third-party elements, you can’t do without SSL.
- Improved search engine ranking. Search engines motivate website owners to certify web projects in their own way. For example, Google directly claims that HTTPS is a ranking factor in search. So, if you don’t want to end up on the fourth page of a search results for your topic, enable SSL.
- Compliance with personal data protection laws. For example, European GDPR law requires legal entities including websites that collect personal data to use encryption. SSL helps meet the requirements of these type of laws.
Types of certificates
Depending on the source of origin, the number of connected domains, as well as validation methods, there are different classifications of certificates.
- Self-Signed. This certificate is signed directly by your server. Any user can generate it by himself. However, there is not much use for it – browsers will still display a notification that the Internet connection is not secure when you access a page with a self-signed certificate.
- Signed by a certification authority (CA). Such certificates are signed by special organizations, which guarantee the authenticity of a digital signature. There are not many certification authorities, the most famous are: COMODO, CloudFlare, LetsEncrypt.
Certificates from certification centers are divided into groups based on the type of data that should be verified in order to obtain it:
- Domain Validation (DV). Basic level. It provides cryptographic encryption and HTTPS connection. But it does not contain proof of the actual existence of the company.
- Organization Validation (OV). Allows establishing an encrypted web connection, but also certifies the validity of the company received this certificate. Only official legal entities can obtain it.
- Extended Validation (EV). The highest level of certification available to online businesses. In order to obtain it, you have to go through extended validation and provide the necessary documentation to prove your rights for the domain name.
Certification Authority also allows you to enable additional options:
- SAN. Upon obtaining a certificate, clients specify a list of domains that will be covered by the certificate.
- WildCard. Certification covers the domain name and all subdomains.
How to choose an SSL certificate?
The choice of certificate should be made based on your business needs. A FinTech project and a landing page for booking a webinar need a different level of SSL certificate. It is preferable to install a certificate before launching a web project. This will help to immediately take more favorable positions in search engines. You can add an HTTPS exchange very quickly, but the Google algorithms may notice it only after several months.
SSL certificates pricing varies from zero to several hundred dollars per year. If you are a local business owner or have a non-profit IT project, you can get a free SSL certificate. However, a large project that involves the processing of personal data and payments – it is recommended to get a paid one. Once you have decided on the number of domains to be connected and the type of verification, you can proceed to selecting a certification authority that offers the required set of services.
How to get a free SSL?
Free SSL certificates mostly belong to the Domain Validation category. They are suitable for small websites which do not ask for any sensitive data, e.g. a credit card number. DV-certificate is suitable for:
- a personal blog;
- a company’s landing page;
- one-page website for registering for an event.
You can get a free SSL certificate from almost any CA. Most of them provide certificates with short validity period. For example, Let’s Encrypt and COMODO offer free DV certificates for 90 days, as well as wildcards. In addition, many hosting providers provide DV certificates in a bundle with your hosting package.
However, DV does not guarantee that the website belongs to a real legal entity. For payment systems, marketplaces and other Internet projects that request banking information, it is better to have OV or EV certification.
How to install an SSL certificate on my website?
To make an SSL certificate working, you need to do the following:
- Preconfigure your server and make sure that the data in the WHOIS section matches the one sent to the CA.
- Create a request for signing the SSL on your server. Your hosting provider can help here.
- Send a request to verify the SSL certificate and information about the organization and domain name.
- Install ready SSL certificate on the site after validation.
Depending on the selected CA and verification method, certificate release may take from several minutes to several weeks (for extended validation).
Summing up
An SSL certificate provides a secure data exchange between a website and a user’s computer. Thanks to cryptography, hackers will not be able to steal your data for their own purposes. It is not only about protection, but also about the trust of your visitors, search engine ranking and possibility of installing additional options.
There are many companies on the market that release SSL. Based on your needs and objectives, you should install an SSL certificate to your website for free or choose a paid one which provides better protection and a range of features.
We are always on duty and ready to assist!
Blog

CDN for streaming services
CDN (Content Delivery Network) is a network infrastructure that optimizes the delivery of data to end users through linked sites or points of presence (PoP) located in different geographic regions. This ensures load balancing by processing requests closer to users, which ultimately provides a faster speed for visitors of a web resource.
How it works
When using regular hosting, the browser of the visitor to the Internet resource interacts directly with the client hosting, where all data is stored. CDN adds intermediate links to this chain in the form of special caching sites scattered around the world.
The network of data centers stores the cache or portions of the files for the quick delivery to end users. And even if the client site is hosted in New York, a visitor from Japan can surf the website with minimal delay, because he will get the cache of the web page from the closest point to him.
Advantages of CDN
The technology has a number of advantages:
- High loading speed. Since the distance between consumers and hosting servers is reduced to a minimum, the response time rarely exceeds a fraction of a second.
- Reducing the load on the main server. Since the traffic is evenly distributed between network elements, client infrastructure is used only for syncing and changing settings.
- Handling of “heavy” media files. Resource-intensive content (e.g., video) is fetched by end-users in batches as it is downloaded. This leads to channel overload, especially if the user’s Internet connection is slow and the content is downloaded in small chunks. With Content Delivery Network, fragments are stored on network servers, which allows you to handle tens or hundreds of thousands of requests, regardless of their size, without lags.
- Fault tolerance. The structure can consist of hundreds of points of presence distributed across countries and continents. With this configuration, the system provides significant redundancy of cached data storage.
- Scalability and reliability. CDN is virtually unlimited in the number of requests and expands as the load increases. The peak of millions of sessions will not affect the availability of information, it will be synchronized without any disruptions. And even in case of an emergency, users will still have access to static content on their local Point of Presence.
Promotion of the site in search results. Long loading of a web page affects user experience, which significantly reduces conversion rates and increases the number of bounces. This leads to a decrease in the search engine ranking. Distribution of requests between data centers improves conversion and, as a consequence, affects the position of the resource in the top search engine.
When CDN is a must-have?
Now, when we know what a CDN is, let’s discuss who needs it. CDN is an excellent choice for IT-projects which have a wide audience from remote corners of the world. This network technology increases reliability and speed of downloading at any volume of incoming stream. It is impossible to imagine a modern game portal, or a popular mobile app without it.
In the last decade, streaming services, which allow you to play information directly from the Internet, have become widespread. Online broadcasting of movies or sports events in good quality, listening to music became a norm for millions of users. Content is no longer stored on devices, it goes online and CDN has become a real salvation for such projects.
However, this approach is not necessary for ordinary websites that don’t involve extensive geography or one-step sending of “heavy” files. A business website of a company operating in the California area which is hosted in Los Angeles doesn’t need a CDN. If you face long “rendering” of your website in the browser, most likely, there is a problem with the code, not with the network.
Specifics of the technology
When using a content delivery network, you should understand the principles of its operation in detail. When choosing a provider, you may encounter different algorithms that determine which data center to contact. They are based on two main web technologies – AnyCast and GeoDNS.
The difference is that with AnyCast, the connection is routed to the closest points of presence at a dedicated address. The website visitor’s ISP receives route announcements to the CDN and provides an optimal path connection. If the connection is lost, the client will connect to the next closest PoP. This technology is based on the BGP protocol, which is the basis of all the redundancy and route selection on the Internet.
With GeoDNS, IP addresses are assigned according to the point of the user’s presence. CDN determines the location of the sender and forwards it to the closest server based on geographic location in accordance with pre-defined rules.
CDN providers. How to choose?
CDN services are provided by a number of local and global companies. To avoid making the wrong choice, you should pay attention to the following:
- Type of content. Different data requires different bandwidths. Streaming and online games require a wider channel than for a static content. However, it will be more expensive.
- Location of the main audience. You need to determine where most of your users are coming from. And then see if there are CDN PoPs in these regions.
- Data transmission security. It is important to make sure that the CDN supports TLS (transport layer security) certificates, and allows you to use your own SSL certificate.
- Flexibility of the settings. The more options you have in your control panel, the more effectively you can optimize traffic routes and increase the speed of delivery.
- Tech support. The speed and proficiency of the support will determine the reliability of your service, and therefore the revenue. Having 24/7 support will be a great option.
- Pricing and a trial period. Pricing and a trial period. For many web projects, the cost becomes a major determining factor. It is better to calculate the estimated budget in advance, taking into account CDN costs. In addition, some providers offer a free trial period to get acquainted with their services.
Melbicom has its own CDN network with data centers located on all continents in 36 countries. We offer caching of static content and video files, full support for the HTTP/2 protocol and detailed statistics for all of our tariffs. Thanks to the brotli-compression protocol, customers and visitors can save a lot of their budgets on traffic.
Summing up the results
What is CDN? It is a great solution, thanks to which a subscriber from Bulgaria can easily watch a new season of “Paper House” on Netflix. Content Delivery Network makes the Internet more accessible. It is becoming the basis of many modern IT solutions: marketplaces, streaming platforms, and game portals. This web technology speeds up site loading and ensures the continuous operation of Internet projects. There are many offers on the market, but if your project is aimed at a small, geographically concentrated audience and does not involve the constant transfer of “heavy” media files, think twice about the reasonability of using CDN. After all, you have to pay for everything.
We are always on duty and ready to assist!
Blog

What is CDN and where it can be used?
CDN (Content Delivery Network) is a network infrastructure that optimizes the delivery of data to end users through linked sites or points of presence (PoP) located in different geographic regions. This ensures load balancing by processing requests closer to users, which ultimately provides a faster speed for visitors of a web resource.
How it works
When using regular hosting, the browser of the visitor to the Internet resource interacts directly with the client hosting, where all data is stored. CDN adds intermediate links to this chain in the form of special caching sites scattered around the world.
The network of data centers stores the cache or portions of the files for the quick delivery to end users. And even if the client site is hosted in New York, a visitor from Japan can surf the website with minimal delay, because he will get the cache of the web page from the closest point to him.
Advantages of CDN
The technology has a number of advantages:
- High loading speed. Since the distance between consumers and hosting servers is reduced to a minimum, the response time rarely exceeds a fraction of a second.
- Reducing the load on the main server. Since the traffic is evenly distributed between network elements, client infrastructure is used only for syncing and changing settings.
- Handling of “heavy” media files. Resource-intensive content (e.g., video) is fetched by end-users in batches as it is downloaded. This leads to channel overload, especially if the user’s Internet connection is slow and the content is downloaded in small chunks. With Content Delivery Network, fragments are stored on network servers, which allows you to handle tens or hundreds of thousands of requests, regardless of their size, without lags.
- Fault tolerance. The structure can consist of hundreds of points of presence distributed across countries and continents. With this configuration, the system provides significant redundancy of cached data storage.
- Scalability and reliability. CDN is virtually unlimited in the number of requests and expands as the load increases. The peak of millions of sessions will not affect the availability of information, it will be synchronized without any disruptions. And even in case of an emergency, users will still have access to static content on their local Point of Presence.
Promotion of the site in search results. Long loading of a web page affects user experience, which significantly reduces conversion rates and increases the number of bounces. This leads to a decrease in the search engine ranking. Distribution of requests between data centers improves conversion and, as a consequence, affects the position of the resource in the top search engine.
When CDN is a must-have?
Now, when we know what a CDN is, let’s discuss who needs it. CDN is an excellent choice for IT-projects which have a wide audience from remote corners of the world. This network technology increases reliability and speed of downloading at any volume of incoming stream. It is impossible to imagine a modern game portal, or a popular mobile app without it.
In the last decade, streaming services, which allow you to play information directly from the Internet, have become widespread. Online broadcasting of movies or sports events in good quality, listening to music became a norm for millions of users. Content is no longer stored on devices, it goes online and CDN has become a real salvation for such projects.
However, this approach is not necessary for ordinary websites that don’t involve extensive geography or one-step sending of “heavy” files. A business website of a company operating in the California area which is hosted in Los Angeles doesn’t need a CDN. If you face long “rendering” of your website in the browser, most likely, there is a problem with the code, not with the network.
Specifics of the technology
When using a content delivery network, you should understand the principles of its operation in detail. When choosing a provider, you may encounter different algorithms that determine which data center to contact. They are based on two main web technologies – AnyCast and GeoDNS.
The difference is that with AnyCast, the connection is routed to the closest points of presence at a dedicated address. The website visitor’s ISP receives route announcements to the CDN and provides an optimal path connection. If the connection is lost, the client will connect to the next closest PoP. This technology is based on the BGP protocol, which is the basis of all the redundancy and route selection on the Internet.
With GeoDNS, IP addresses are assigned according to the point of the user’s presence. CDN determines the location of the sender and forwards it to the closest server based on geographic location in accordance with pre-defined rules.
CDN providers. How to choose?
CDN services are provided by a number of local and global companies. To avoid making the wrong choice, you should pay attention to the following:
- Type of content. Different data requires different bandwidths. Streaming and online games require a wider channel than for a static content. However, it will be more expensive.
- Location of the main audience. You need to determine where most of your users are coming from. And then see if there are CDN PoPs in these regions.
- Data transmission security. It is important to make sure that the CDN supports TLS (transport layer security) certificates, and allows you to use your own SSL certificate.
- Flexibility of the settings. The more options you have in your control panel, the more effectively you can optimize traffic routes and increase the speed of delivery.
- Tech support. The speed and proficiency of the support will determine the reliability of your service, and therefore the revenue. Having 24/7 support will be a great option.
- Pricing and a trial period. Pricing and a trial period. For many web projects, the cost becomes a major determining factor. It is better to calculate the estimated budget in advance, taking into account CDN costs. In addition, some providers offer a free trial period to get acquainted with their services.
Melbicom has its own CDN network with data centers located on all continents in 36 countries. We offer caching of static content and video files, full support for the HTTP/2 protocol and detailed statistics for all of our tariffs. Thanks to the brotli-compression protocol, customers and visitors can save a lot of their budgets on traffic.
Summing up the results
What is CDN? It is a great solution, thanks to which a subscriber from Bulgaria can easily watch a new season of “Paper House” on Netflix. Content Delivery Network makes the Internet more accessible. It is becoming the basis of many modern IT solutions: marketplaces, streaming platforms, and game portals. This web technology speeds up site loading and ensures the continuous operation of Internet projects. There are many offers on the market, but if your project is aimed at a small, geographically concentrated audience and does not involve the constant transfer of “heavy” media files, think twice about the reasonability of using CDN. After all, you have to pay for everything.