Blog

MongoDB vs. SQL: Choosing the Right Database Hosting
A dozen years ago the NoSQL-versus-relational argument was a winner-takes-all brawl. Reality intervened. By the mid-2020s only 8 % of engineering teams rely solely on NoSQL, while 49 % operate mixed fleets . The question is no longer which model wins but how to balance agility, consistency, and scale—then host the result on reliable infrastructure that never blinks.
This guide compares the two models around four pillars—data model, scaling topology, schema philosophy, and feature convergence—and closes with hosting patterns that exploit Melbicom’s global dedicated-server footprint.
Choose Melbicom— 1,300+ ready-to-go servers — 21 global Tier IV & III data centers — 55+ PoP CDN across 6 continents |
 |
What’s the Difference Between Document and Tabular Models?
Relational tables enforce typed columns, keys, and constraints. Decades of query-planner research let a single SQL statement join 20 tables and stream aggregates in milliseconds. In turn, schema changes require migrations and downtime planning.
Document stores such as MongoDB treat each BSON document as a self-contained record: schemas may differ, nested arrays replace joins, and new fields ship with the next deploy.
| Model | Strengths | Trade-offs |
|---|---|---|
| Tabular (SQL) | ACID, mature JOIN/aggregate engine, static typing | Slower schema evolution; multi-node write scale is complex |
| Document (MongoDB) | Schema agility, high write throughput, hierarchical reads | Joins less efficient; integrity rules shift to application |
Hybrid adoption is now normal: finance ledgers in PostgreSQL; content metadata in MongoDB. 49 % of organizations run at least one SQL and one NoSQL engine —proof that polyglot persistence is the mainstream path.
Sharding vs. Clustering: How Do You Scale MongoDB and SQL?
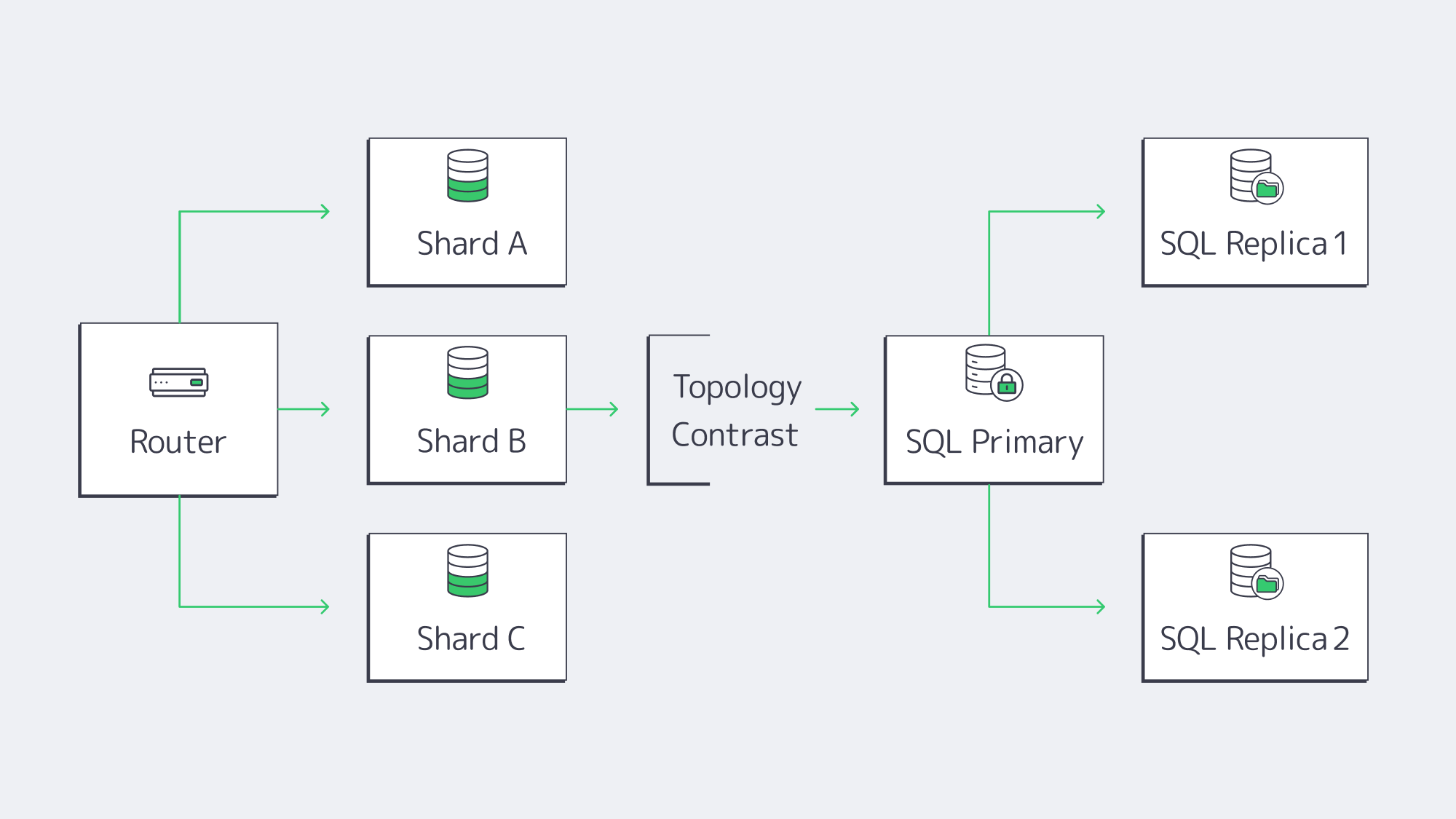
- MongoDB sharding automatically partitions collections by a shard key, balances chunks across servers, and scales writes linearly—petabyte datasets and six-figure TPS are routine. Replica sets add fail-over with a few configuration flags.
- Relational engines historically scaled up (more CPU, RAM, and NVMe). Read replicas handle analytics, and manual partitioning spreads writes. “Distributed SQL” products mimic Mongo-style sharding, but adoption is early.
Topology drives hosting: a sharded MongoDB fleet may span half-a-dozen mid-grade servers; a mission-critical SQL system often lives on one giant node plus synchronous replicas. Cost is context-specific. Three 8-core MongoDB nodes can undercut a 64-core SQL box if licenses are factored in; the reverse is true when SQL Server cores are already owned. Smart DBAs run a quick spreadsheet before committing.
Flexible Schemas vs. ACID: When Should You Prioritize Each?
MongoDB’s schema-on-read lets developers add attributes without running ALTER TABLE, shaving weeks off large-scale migrations. OTTO—one of Europe’s largest e-commerce marketplaces—cut product-catalog refresh times from 12 hrs to 15 mins after adopting MongoDB, yet it may later have spent days cleansing documents that lacked newly required compliance flags. Flexibility, in other words, still demands strong governance.
Relational databases refuse malformed data and guarantee ACID transactions. Financial transfers or inventory debits either complete entirely or roll back—no phantom states .
The gulf has narrowed. MongoDB added multi-document ACID transactions in 4.0 (replica sets) and 4.2 (shards) . Conversely, PostgreSQL, MySQL 8.0, and SQL Server 2022 store and index JSON nearly as fast as native document stores . Architects can now dial flexibility and rigor per collection or table: money flows stay in SQL, polymorphic user data in MongoDB, validation in APIs, and correlation IDs tie the story together.
Convergence Features—Transactions & JSON Everywhere
- Analytics in MongoDB –
$lookup joins, window functions, and time-series buckets narrow the query gap. - SQL JSON – PostgreSQL 15’s
jsonb_path_opsindexes shave 30 % off key-path lookups; SQL Server 2022 builds computed indexes on JSON paths. - Vector & graph – pgvector and MongoDB Atlas Vector Search arrived in 2024 for AI similarity retrieval workloads.
- Consensus replication – Raft algorithms deliver predictable fail-over on either platform.
Selection is therefore less about missing features and more about ergonomics: document stores excel at sparse datasets, relational engines dominate deep joins and ad-hoc analytics at scale today.
Decision Framework for Modern Deployments
| Criterion | Lean Document | Lean Relational |
|---|---|---|
| Data shape | Polymorphic, nested | Highly normalized |
| Query profile | Simple key lookups | Multi-table joins |
| Consistency | Eventual acceptable | Strong required |
| Growth | Horizontal writes | Vertical or distributed-SQL |
| Licensing | SSPL/FOSS | FOSS or $$$ |
| Ops skill | Dev-led JSON | DBA-led SQL |
MongoDB Database Hosting: Why Do Dedicated Servers Matter?

Databases are sensitive to jitter. Multi-tenant clouds hide hypervisors and shared disks that can spike latency 10×. Dedicated hardware restores determinism:
- Local NVMe > 3 GB/s; cloud network volumes may cap at 500 MB/s.
- Full CPU cache means consistent query plans; no stolen cycles.
- Kernel tuning—
nonescheduler, huge pages—requires root, which bare metal provides.
We at Melbicom supply 1,300+ ready-to-go dedicated server configurations across 21 global data centers. MongoDB shards in Paris, SQL replicas in Los Angeles, private backbone in between—24 × 7 support swaps any failed hardware while DBAs sleep.
Cost Dynamics of Dedicated vs Cloud for Database Loads
Storage and I/O remain the stealth budget killers. A sharded MongoDB pipeline that ingests 30 TB of event data every month can still generate $20 k–30 k in cloud I/O fees, while a heavy Microsoft SQL Server instance on a supersized VM can ring up $0.20 per log write once tempdb starts thrashing. By contrast, a fixed-price dedicated server bakes the cost of high-end NVMe into one predictable monthly bill—no metered surprises.
Many architects begin their cost research with the evergreen query “how much does Microsoft SQL Server cost?” and quickly discover that license fees stack on top of cloud charges. Upgrading directly to SQL Server 2022—and running it on Melbicom hardware with all cores properly licensed—often proves cheaper and far safer than maintaining any out-of-support edition.
Separately from databases, Melbicom amplifies savings with 55+ CDN PoPs: static assets stay at the edge—independent of the database path—reducing application egress. For database traffic itself, replicas syncing between Paris and Madrid traverse our private backbone, not the public Internet, keeping replication low-latency and predictable.
Operational Playbooks and Tooling
Bare-metal no longer means hand-crafted scripts. Ansible, Terraform, and Kubernetes bare-metal operators cover day-0 through day-n. Melbicom’s API exposes IPMI and power-cycling endpoints so DevOps can automate reboots; IP block management, image loads, and IP failover can be integrated via customer tooling or handled through support workflows. TLS certs can auto-renew, metrics can ship to Grafana, and RAID rebuilds can alert PagerDuty—all while packets stay inside the data-center copper. You gain private-cloud ergonomics with public-cloud speed—a distributed-cloud operating model.
Hosting Patterns at a Glance
| Pattern | Typical Nodes | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Single Powerful SQL Box | 1 × 32–64 core, 256 GB RAM | High-value OLTP & analytics |
| MongoDB Sharded Cluster | 3 config + N shards, 8–16 core each | Write-heavy, unstructured data |
| Polyglot Mesh | Mix behind 10 GbE | Apps needing both models |
Conclusion—Agility, Consistency, Scale: Pick Two, Host Smart

Modern database engineering is about compromise. MongoDB accelerates development and horizontal growth, while SQL engines guarantee incorruptible state and slice data from every angle. Feature convergence softens extremes, yet each model retains superpowers the other only emulates. The decisive factor is operational: align engine strengths with infrastructure that delivers deterministic performance and transparent economics.
Deploy dedicated servers today
Spin up high-performance dedicated servers worldwide in minutes—no setup fees, no surprises.